- CVS
http://www.march-hare.com/cvspro/
http://savannah.nongnu.org/projects/cvs
- SVN
http://subversion.apache.org/
- GIT
GitHub is the best way to collaborate with others. Fork, send pull requests and manage all your public and private git repositories.
http://git-scm.com/
- What is Git
fork
A fork is a
A clone is not a fork; a clone is a local copy of some remote repository. When you clone, you are
A branch is a mechanism to handle the changes within a single repository in order
What's the difference between a "pull request" and a "branch"?
A branch is just a separate version of the code.
A pull request is when someone takes the repository, makes their own branch, does some changes, then tries to merge that branch in (put their changes in the other person's code repository).
What is the difference between "git pull" and "git fetch"?
git pull does a git fetch followed by a git merge.
When you use
When you fetch, Git gathers any commits from the target branch that do not exist in your current branch and stores them in your local repository. However, it does not merge them with your current branch. This is
How to revert previous commit in git?
git reset
git reset HEAD~1
git status
git reset
What is "git cherry-pick
The command git cherry-pick
git cherry-pick <commit-hash>
Tell me the difference between HEAD, working tree and index, in Git?
The working tree/working directory/workspace is the directory tree of (source) files that you see and edit.
The index/staging area is a single, large, binary file in <
HEAD is a reference to the last commit in the
Could you explain the
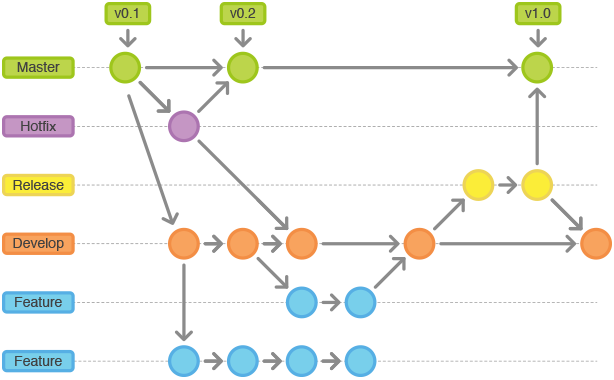
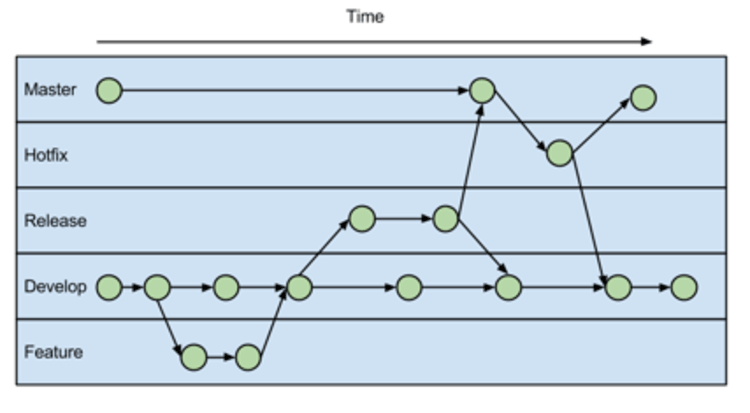
Master - is always ready to
Develop - is the branch to which all feature branches
Feature - Each new feature should
When should I use "
The git stash command takes your uncommitted changes (both staged and unstaged), saves them away for later use, and then reverts them from your working copy.
git status
git stash
git status
# Assume the latest commit
# start working on the next
# stash away the current mess I made
$ git stash save
# some changes in the working dir
# and now add them to the last commit:
$ git add -u
$ git commit
# back to work!
$ git stash pop
How to remove a file from git without removing it from your file system?
If you are not careful during a git add, you may end up adding files that you didn’t want to commit. However, git
git reset filename # or
echo filename >>
When do you use "
With rebase you say to use another branch as the new base for your work.
git merge master
git rebase master
Is the branch you are getting changes from shared with other developers outside your team (e.g. open source, public)? If so, don't rebase. Rebase destroys the branch and those developers will have broken/inconsistent repositories unless they use git pull
How skilled is your development team? Rebase is a destructive operation. That means, if you do not apply it correctly, you could lose committed work and/or break the consistency of other developer's repositories.
Does the branch itself represent useful information? Some teams use the branch-per-feature model where each branch represents a feature (or
Might you want to revert the merge for any reason? Reverting (as in undoing) a rebase is considerably difficult and/or impossible (if the rebase had conflicts) compared to reverting a merge. If you think
https://www.codementor.io/alexershov/11-painful-git-interview-questions-and-answers-you-will-cry-on-lybbrqhvs
- The
Gitflow
This workflow doesn’t add any new concepts or commands beyond what’s required for the Feature Branch Workflow.
Instead, it assigns very specific roles to different branches and defines how and when they should interact.
The git-flow toolset is an actual
Git-flow is a wrapper around Git. The git flow init command
Develop and Master Branches
Instead of a single master branch, this workflow uses two branches to record the history of the project. The master branch stores the official release history, and the develop branch serves as an integration branch for features. It's also convenient to tag all commits in the master branch with a version number.
https://www.atlassian.com/git/tutorials/comparing-workflows/gitflow-workflow
- The core idea behind the Feature Branch Workflow is that all feature development should take place in a dedicated branch instead of the master branch. This encapsulation makes it easy for multiple developers to work on a particular feature without disturbing the main
codebase
https://www.atlassian.com/git/tutorials/comparing-workflows/feature-branch-workflow
- What is Git
–
Git plays a vital role
Tools like Git enable communication between the development and the operations team. When you are developing a large project with a huge number of collaborators, it is very important to have communication between the collaborators while
https://www.edureka.co/blog/what-is-git/
- What is the difference between Git and SVN?
Git is a Decentralized Version Control tool
Clients can clone entire repositories on their local systems
Commits are possible even if offline
SVN is a Centralized Version Control tool
Only online commits
What is ‘bare repository’ in Git?
A “bare” repository in Git just contains the version control information
A
A working tree, or checked out copies of your project files.
In Git how do you revert a commit that has already
There can be two answers to this question
Remove or fix the bad file in a new commit and push it to the remote repository. This is the most natural way to fix an error.
Create a new commit that undoes all changes that
git revert <name of bad commit>
What is the difference between git pull and git fetch?
Git pull command pulls new changes or commits from a particular branch from your central repository and updates your target branch in your local repository.
When you perform a
If you want to reflect these changes in your target branch,
Git pull = git fetch + git merge
What is ‘staging area’ or ‘index’ in Git?
That before completing the commits, it can
What is Git stash?
Stashing takes your working directory that is, your
Often, when you’ve been working on part of your project, things are in a messy state and you want to switch branches for sometime to work on something else. The problem is, you don’t want to do a commit of half-done work just so you can get back to this point later. The answer to this issue is Git stash.
How do you find a list of files that has changed in a particular commit?
git diff-tree -
How do you squash last N commits into a single commit?
There are two options to squash last N commits into a single commit
If you want to write the new commit message from scratch use the following command
git reset
git commit
If you want to
git reset
git commit
What is Git bisect?
This command uses a binary search algorithm to find which commit in your project’s history introduced a bug
Describe branching strategies you have used?
Feature branching
A feature branch model keeps
Task branching
In this model
Release branching
Once the develop branch has
How will you know in Git if a branch has already
git branch
git branch
What is Git rebase and how can it
If a feature branch
https://www.edureka.co/blog/interview-questions/git-interview-questions/
- Git is a revision control system, a tool to manage your source code history. GitHub is a hosting service for Git repositories
In the SVN analogy, Git replaces SVN, while GitHub replaces SourceForge
If this project of yours is new, then you can still commit to your local Git, then you can push to GitHub later on. You will need to add your GitHub repo as a 'remote repository' in your Git setup.
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/13321556/difference-between-git-and-github
- What branching strategy to use? Should develop branch be stable or not, or to what extent it should be stable
Or
So the only viable option is to test those features in their branches and merge into the main branch subsequently, so that there is no way they could unpredictably interfere with each other, but more on testing in the following section.
Typical approach
You write some code, probably with some unit tests. You have no confidence that everything works fine though. Anyway, by the time when you’re done with your user-story you can’t be sure that everything works as expected and you
The better option, as mentioned earlier, is to merge it right away into develop
It just
Do you recognize what branching strategy corresponds to this workflow? Right, it’s
Deployment
Do you deploy manually? Automatically? How long does it take? Are you ready to deploy every commit in the main branch? If
https://hackernoon.com/gitflow-is-a-poor-branching-model-hack-d46567a156e7
post-release testing and bug-fixes
feature branch workflow with additional branches dealing with post-release testing and bug-fixes
master branch -> production code
develop branch -> all code developed but not released yet
release branch -> testing purposes by QA team, keeping history of code base, document/hold specific releases
hot fix branch -> quick fix to production code,document /hold hot fixes history/log, hot fix branch branches off from master or release branches
feature branch -> all code currently being developed
scenario-1
branch off into the release branch to the develop branch
scenario-2
bug is found by QA team testing release branch.
branch off into hot fix branch from the release branch, fix bug and merge it back to the release branch
scenario-3
release the code to the customer
keep repository up-to-date
marking point in the repository history
scenario-4
branch off into hot fix branch, fix bug and merge it back to master branch
- IBM
ClearCase
http://www-01.ibm.com/software/awdtools/changemgmt/features/
- Visual
SourceSafe
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms181038%28v=VS.80%29.aspx
- Team Foundation Server
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Team_Foundation_Server
- Java CSV Library
Java CSV is a small fast open source java library for reading and writing CSV and plain delimited text files. All kinds of CSV files can
http://sourceforge.net/projects/javacsv
- Version control is
incredibly important, especially in today's high-paced environment with increasingly shorter product release cycles. By tracking changes across all software assets and facilitating seamless collaboration, a version control system allow development and DevOps teams to build and ship better products faster.
UberSVN
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/UberSVN
- Subversion is a leading and fast growing Open Source version control system.
SVNKit brings Subversion closer to the Java world!SVNKit is a pure Java toolkit
https://svnkit.com/
- Subversive -
JavaHL -SvnKit
The two connectors should both work, here are the differences (more from experience by using them, not by reading their source code):
SVN Kit:
Works on all platforms, is a Java-only implementation (no need for DLLs or shared libraries).
Is a
Keeps its configuration at some other place than a real subversion client like
Needs a shared library (DLL), that has the same major version as the installed Subversion client. So if you use SVN command client 1.6
Is easy to use under Windows, more difficult to find the right version for Linux or Mac OS X
Is faster and uses the same configuration as the installed SVN command client or
So you may install
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/7703377/which-subversive-connector-discovery-to-use
- Version Control
Version control tracks changes to source code or any other files
A good version control system can tell you
It allows a software developer to undo any changes to the code, going back to any prior version, release, or date.
This can be
the version number
Version control also provides a mechanism for incorporating changes from multiple developers, an essential feature for large software projects or any projects
with geographically remote developers
repository
working copy
check-out
check-in
push
pull
diff
update
conflict
The basic steps that one would use to get started with a centralized version control system (such as Subversion/SVN) are
1. Create a repository
2. Import a directory structure and/or files into the repository
3.
4. Edit/
between the working copy and the repository (i.e., diff)
5. Check-in (or commit) the changes to the repository
The basic steps that one would use to get started with a distributed version control
system (such as Git) are
1. Create an original “master” repository
2. Clone the repository to allow development
3. Add a directory structure and/or files into the local repository
4. Check-in or “commit” the directory structure and/or files to the local
repository
5. Push these modifications of the local repository into the master repository
6. Edit/
between the
7. Check-in or “commit” the file modifications to the local repository
8. Pull any modifications from the original repository into the local repository
(in case someone has
9. Push these modifications of the local repository into the master repository
Version Control Tutorial using
Christopher J. Roy, Associate Professor
Tortoise-SVN-Git-Tutorial.pdf
- The Revision Control System (RCS) manages multiple revisions of files.
RCS is useful for text that
https://www.gnu.org/software/rcs/
Trunk would be the main body of development, originating from the start of the project until the present.
Branch will be a copy of code derived from a certain point in the trunk that
Tag will be a point in time on the trunk or a branch
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/16142/what-do-branch-tag-and-trunk-mean-in-subversion-repositories
- Using Subversion
Server can have an unlimited number of "repositories".
Work cycle
-create
-make changes
-see what's changed meanwhile
-update your local copy
-resolve conflicts-merge your changes
-submit your changes
Logging a Revision
Content what has changed?
Date when did it change?
Author who changed it?
Reason
List files in the repository:
>
Change to a suitable directory
> cd d:\workspace
check out the "trunk" to a directory named "demo"
>
"Conflict" means you have
So there is a "conflict" between your work and work already in the repository.
Subversion client creates 4 files when a conflict exists.
Edit-Conflict tool of
The choices are:
(1)
(2) accept remote, discard your local changes.
(3) override remote, use your local changes.
After resolving all conflicts, mark the file as "resolved".
Subversion will delete the extra 3 copies.
"Importing" a Project
The initial check-in of code into subversion
Decide what not to import. Examples:
compiler output (*.class, *.obj, *.exe)
large image files, video, other "data"
3rd party libraries you can get from Internet, e.g. log4j.jar,
if you need an online copy of 3rd party libraries, put them in a separate project and link it as an "external" in your project
In the project root directory create a file named
Put any file patterns (including "*" wildcard) and names of directories
*.obj
*.class
*.bak
Eclipse and other IDE automatically ignore most of these (bin, dist, build).
Import your project directory into a "trunk" directory inside repository:
cmd> cd
cmd>
cmd>
cmd>
For
http://servername/svn/myproject/trunk
http://servername/svn/myrepo/myproject/trunk
Why do we need
Mark a release version of a product.
Mark a snapshot of the current development.
Typical Release names:
Release-1.0.0
REL-0.3.0RC1
A Tag name must be unique.
Contents of a "tag" should not
Tagging by Copy: command line
If
Why Branching?
This could happen to you:
You create a great product and
Before you delivered the
Your development team is
And now Murphy
Customer reports that he found a major bug in your software!
The development has continued after the release of REL-1.0.0
You want to fix the bug to satisfy your customer!
In your current development you have enhanced many of the product’s functions but you don‘t want to deliver
How to solve this situation?
Based on the tag you
You create a Branch to fix the bug in the software.
RELEASE 1.0.0 -> BUGFIX_BRANCH
After you have fixed the bug
you can tag the Branch and deliver another version to the customer.
BUGFIX_BRANCH->RELEASE 1.0.1
You haven
You can create a branch using the following command:
Based on your company’s policy you may have subdirectories under the branches directory in the repository:
branches/release-candidates
branches/sub-projects
branches/user-branches
You would like to work on the branch to fix the bug
You can do it in two ways:
Check out a complete new working copy from the branch.
switch your current working copy to the particular branch.
You can switch your current working copy to a branch with the following command:
Fix the bug through doing the
After having fixed the bug on the branch create a tag to mark the new release which can
Create the new Release Tag:
Merging From a Branch
What’s with the bug you've fixed on the bug-fix-branch?
What about your current development?
RELEASE 1.0.0 -> BUGFIX_BRANCH ->RELEASE 1.0.1->MERGE BACK TO TRUNK
You can merge the changes from the branch into your current working copy with the following command
The revision in which we created the branch (267) and HEAD for the complete branch.
You can find the revision number when the branch
Merge tracking:
Subversion does not have any function to track merges that have already
i.e., to prevent you to merge a branch a second time.
Example: after merging, create a README-merged file in the branch stating that
The intention of a tag is that it should
Version Control Best Practices
Plan the directory structure
Decide what work products to put in version control
Decide what to exclude
Big decision: repository layout
one "project" per repo?
many projects per repo?
Example: separate Eclipse projects for "core", "web", and "web services" components of your software
Commit all files related to the same task as one commit.
This makes comments more meaningful.
Create a tag for each milestone and each release.
Create branches for experimental work and bug fixes.
Avoid too many branches.
Developer Branches
One branch per team member or several members on a branch - the decision
Advantages using branches for team work:
No changes during development on the main line needed => Code stability.
Every team member can work in its own environment
Disadvantages:
Sometimes the mainline and the branch will diverge if the branch lives too long.
Feature Branches
Separation by features (one branch each).
Using Subversion -
- How CVS works? An example of team collaboration in Eclipse
Trunk is the main version of a project.
There is one and only one trunk for each CVS repository
http://www.programcreek.com/2012/04/how-cvs-works-example-of-team-collaboration-in-eclipse/
- Tagging is useful anytime you want a snapshot in time of the state of your project.
http://www.se.rit.edu/~se361/Activities/
- Difference between trunk, tags and branches in SVN or Subversion source control system
In short
- A trunk in SVN is
- A branch in SVN is sub development area where parallel development on different functionalities happens. After completion of a functionality,
- A tag in SVN
- division
is purely based on how programmer usestrunk and branches.
Main difference between branch and tag in subversion is that, tag is
http://javarevisited.blogspot.com/2013/04/difference-between-trunk-tags-and-branch-svn-cvs-git-scm-subversion.html#ixzz2h72XRAOi
- Branching lets you manage different versions of your code base in parallel for things
like maintaining older versions, the development of new features and so on.
But no sooner do you
http://blog.daemon.com.au/go/blog-post/merging-with-subversion-and-eclipse
No comments:
Post a Comment