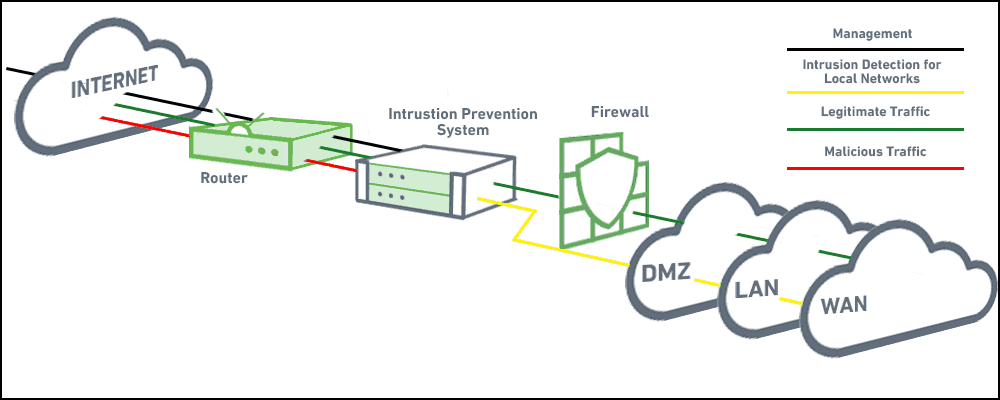
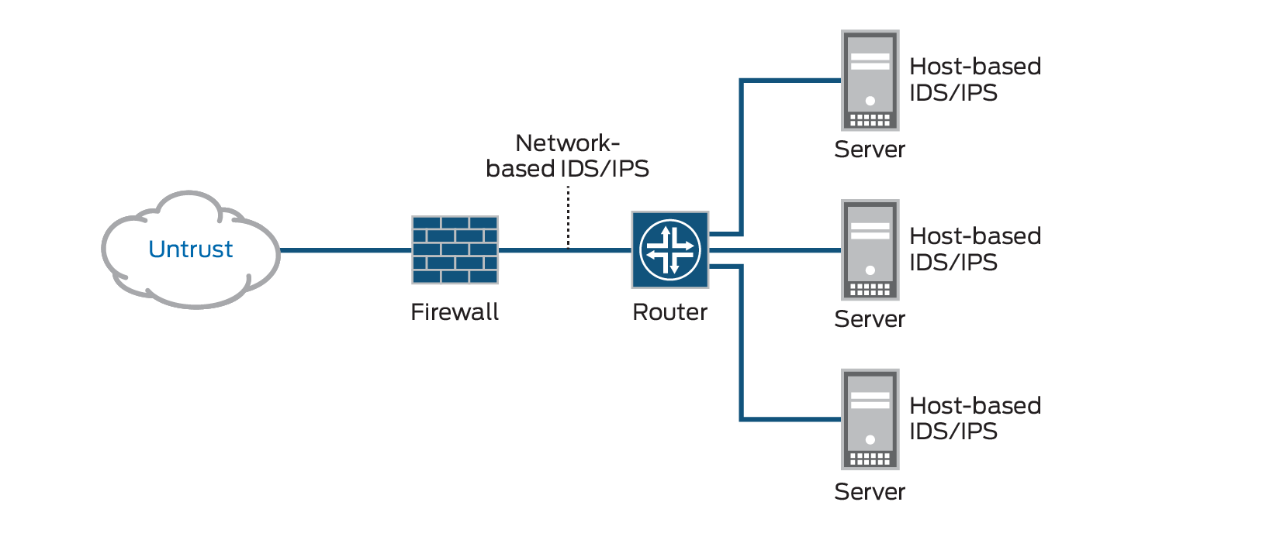
- Intrusion detection system
An intrusion detection system (IDS) is a device or software application that monitors network or system activities for malicious activities or policy violations and produces reports to a management station. IDS come in a variety of “flavors” and approach the goal of detecting suspicious traffic in different ways. There are network based (NIDS) and host based (HIDS) intrusion detection systems.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intrusion_detection_system
- Intrusion prevention system
Intrusion prevention systems (IPS), also known as intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS), are network security appliances that monitor network and/or system activities for malicious activity. The main functions of intrusion prevention systems are to identify malicious activity, log information about this activity, attempt to block/stop it, and report it
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intrusion_prevention_system
firewall prevents malicious traffic
Passive IDS: the IDS only reports that there was an intrusion.
Active IDS: the IDS also takes actions against the issue to fix it or at least lessen its impact.
Firewall - A device or application that analyzes packet headers and enforces policy based on protocol type, source address, destination address, source port, and/or destination port.
Packets that do not match policy are rejected
Intrusion Detection System - A device or application that analyzes whole packets, both header and payload, looking for known events. When a known event
is detected a log message is generated detailing the event.
Intrusion Prevention System - A device or application that analyzes whole packets, both header and payload, looking for known events. When a known event
is detected the packet is rejected.
The IDS only monitors traffic. The IDS
contains a database of known attack signatures. And it compares the inbound traffic against to the database. If an attack
is detected then the IDS reports the attack.
http://security.stackexchange.com/questions/44931/difference-between-ids-and-ips-and-firewall
- The differences between an IDS and a firewall are that the latter prevents malicious traffic, whereas the IDS:
Passive IDS: the IDS only reports that there was an intrusion.
Active IDS: the IDS also takes actions against the issue to fix it or at least lessen its impact.
However, what's the difference between an IPS and a Firewall? Both are a preventative technical control whose purpose is to guarantee that incoming network traffic is legitimate.
Firewall - A device or application that analyzes packet headers and enforces policy based on protocol type, source address, destination address, source port, and/or destination port.
Packets that do not match policy are rejected.
Intrusion Detection System - A device or application that analyzes whole packets, both header and payload, looking for known events. When a known event
is detected a log message is generated detailing the event.
Intrusion Prevention System - A device or application that analyzes whole packets, both header and payload, looking for known events. When a known event
is detected the packet is rejected.
http://security.stackexchange.com/questions/44931/difference-between-ids-and-ips-and-firewall
IPS’s deal with packets, while WAF’s work within sessions
WAFs must understand not just protocol behavior, like HTTP GET, POST, HEAD, etc, but also JavaScript, SQL, HTML, XML, Cookies, etc. This application layer logic is fundamental to the operation of a WAF but not required for IPS functionality, and therefore not typically implemented on an IPS
Baselining is available on IPS and WAF, but the similarity stops with the name. IPS
baselining consists of statistical deviations in
throughput and traffic flows. WAF
baselining involves URL, Parameter, HTTP Method, Session, and Cookie mapping. A WAF knows no concept of bandwidth utilization for
baselining, just an IPS doesn’t know
if a given URL is supposed to accept HTTP POSTs or GETs.
IPS signatures
are looked at by companies
as a means to virtually patch their PC’s ahead of an actual being patch or update being available or fully rolled out. This level of protection isn’t available on an IPS when specific application-layer vulnerabilities exist or when custom written web-application code has some new vulnerability. This is where the WAF provides a measure of protection not available on an IPS,
due to the application-awareness of the WAF.
WAF deployments are focused on web applications and web application traffic, while
IPS deployments are typically done at the network level inspecting all packets.
https://practical.
wordpress.com/2009/12/28/waf-vs-ips-or-four-things-your-ips-cant-do/
- Security: IDS vs. IPS Explained
an IPS has all the features of a good
IDS, but can also stop malicious traffic from invading the enterprise.
In addition, an IPS can respond to a detected threat in two other ways. It can reconfigure other security controls, such as a firewall or router, to block an attack. Some IPS devices can even apply patches if the host has particular vulnerabilities. In addition, some IPS can remove the malicious contents of an attack to mitigate the packets, perhaps deleting an infected attachment from an email before forwarding the email to the user.
http://www.comparebusinessproducts.com/fyi/ids-vs-ips
- Intrusion Detection FAQ: What is the difference between an IPS and a Web Application Firewall?
An IPS
generally sits
in-line and watches network traffic as the packets flow through it. It acts similarly to an Intrusion Detection System (IDS) by trying to match data in the packets against a signature database or detect anomalies against what
is pre-defined as "normal" traffic
WAFs are designed to protect web applications/servers from web-based attacks that IPSs cannot prevent. In the same regards as an IPS, WAFs can be
network or host based. They sit in-line and monitor traffic to and from web applications/servers.
Basically, the difference is in the level of ability to analyze the Layer 7 web application logic.
https://www.sans.org/security-resources/idfaq/ips-web-app-firewall.php
- Perimeter’s Host Intrusion Detection and Prevention System (HIDS/HIPS) is our premier
service designed to protect your most critical data and servers on your network. It
provides an additional layer of defense beyond services such as a managed firewall,
Network Intrusion Prevention Systems (NIPS) and signature-based
anti virus software.
HIDS/HIPS relies on a learning pattern for both known and unknown types of malicious
activity. Rather than relying on signature matching for specific attacks, the behavior-
based rules associated with HIDS/HIPS products monitor and deny malicious activity
patterns. HIDS/HIPS monitors and alerts security operations personnel if activity is
suspicious
http://www.falkensecurenetworks.com/PDFs/HIDS-HIPS[1].pdf
- Host based intrusion detection (HIDS) refers to intrusion detection that takes place on a single host system. Currently, HIDS involves installing an agent on the local host that monitors and reports on the system configuration and application activity. Some common abilities of HIDS systems include log analysis, event correlation, integrity checking, policy enforcement, rootkit detection, and alerting1. They often also have the ability to baseline a host system to detect variations in system configuration.
https://www.sans.org/security-resources/idfaq/what-is-a-host-intrusion-detection-system/1/24
- "OSSEC is an Open Source Host-based Intrusion Detection System. It performs log analysis, file integrity checking, policy monitoring, rootkit detection, real-time alerting and active response. It runs on most operating systems, including Linux, MacOS, Solaris, HP-UX, AIX and Windows.
http://ossec.github.io/
- The Samhain host-based intrusion detection system (HIDS) provides file integrity checking and log file monitoring/analysis, as well as rootkit detection, port monitoring, detection of rogue SUID executables, and hidden processes.Samhain been designed to monitor multiple hosts with potentially different operating systems, providing centralized logging and maintenance, although it can also be used as a standalone application on a single host.Samhain is an open-source multiplatform application for POSIX systems (Unix, Linux, Cygwin/Windows).
http://la-samhna.de/samhain/index.html
- HIDS vs NIDS and which one is better and why?
It’s just that the placement in different. HIDS is placed on each host whereas NIDS is placed in the network. For an enterprise, NIDS is preferred as HIDS is difficult to manage, plus it consumes processing power of the host as well.
https://www.greycampus.com/blog/information-security/top-cyber-security-interview-questions
Snort® is an open source network intrusion prevention and detection system (IDS/IPS) developed by Sourcefire.
http://www.snort.org/
- Differences Between IPS and Firewalls
An IPS will inspect content of the request and be able to drop, alert, or potentially clean a malicious network request based on that content.
A firewall will block traffic based on network information such as IP address, network port and network protocol.
https://its.umich.edu/enterprise/wifi-networks/network-security/ips-vs-firewalls
- A firewall permits and blocks traffic by port/protocol rules. However, an attacker can use legitimate ports to send illegitimate traffic. An IPS looks at the contents of the packets and/or can correlate over time to determine if an attack is happening. An IPS works in tandem with a firewall to make sure that the traffic the firewall permitted is actual legitimate traffic.
https://learningnetwork.cisco.com/s/question/0D53i00000KstPg/ips-vs-firewall