- Traffic policing propagates bursts. When the traffic rate reaches the configured maximum rate, excess traffic
is dropped retains
- Shaping is a QoS (Quality of Service) technique
that we can use to enforce lowerbitrates than what the physical interface is capable of. Most ISPs will use shaping or policing to enforce “traffic contracts” with their customers.
- A broadband remote access server (BRAS, B-RAS or BBRAS) routes traffic to and from broadband remote access devices
such as digital subscriber line access multiplexers (DSLAM) on an Internet service provider's (ISP) network.
The BRAS
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Broadband_remote_access_server
- What is Traffic Shaping?
Traffic shaping (also known as packet shaping) is bandwidth management technique that delays the flow of certain types of network packets
The most common type of traffic shaping is application-based traffic shaping. Fingerprinting tools are first used to identify the application associated with a data packet. Based on this,
Many application protocols use encryption to circumvent application-based traffic shaping. To prevent applications from bypassing traffic shaping policies, route-based traffic shaping can
Limited network resources make bandwidth prioritization a necessity. Traffic shaping is
https://www.barracuda.com/glossary/traffic-shaping
- Traffic shaping, also known as packet shaping, is a
type of is forwarded is rate
Traffic shaping techniques are core components of most network architectures. The benefits of traffic shaping include converging network technologies into a common network architecture and guaranteeing performance requirements for
Quality of Service (QoS) is a specific implementation of network traffic shaping.
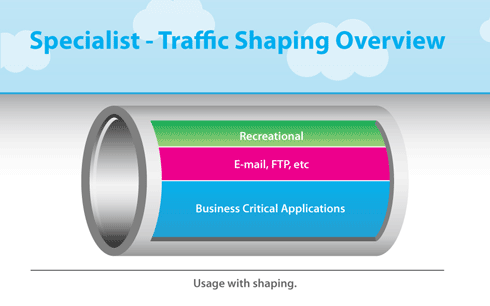
Data Center LAN Networks
Data Center LAN Networks include traffic categories including:
High-Priority
Network traffic to network storage and for database transactions require low-latency network performance with high reliability. These network applications are highly sensitive to network performance and do not tolerate dropped packets well.
Storage Systems
Database Systems
Medium-Priority
User access to business applications are business critical, but do not have the performance and reliability requirements as Storage and Database systems.
User access to Applications
IP Telephony
Low-Priority
Bulk data transfers will completely consume the bandwidth of a network. If
Large file copies
Data backups
Peer-to-Peer applications
https://www.a10networks.com/blog/traffic-shaping/
- During penetration testing, the main
objective it is required be exploited is required at the same time
Active Fingerprinting
Active fingerprinting
Passive Fingerprinting
also maintains a database for
It
https://resources.infosecinstitute.com/passive-fingerprinting-os/#gref
Taxonomy of OS fingerprinting tools
- Active Fingerprinting
Active fingerpringinting
Xmas attack. This is a specific type of specailly
Port scanning. A port scanner sends queries on specific ports. If the server answers a query on a port, it indicates indicates be sent
Passive Fingerprinting
Passive fingerprinting uses a sniffer (such as Wireshark instead passive fingerprinting cannot be done be done
https://blogs.getcertifiedgetahead.com/active-fingerprinting-passive-fingerprinting/