The key elements of ITIL 4 are the four dimensions, the guiding principles, the move from processes to practices, and the Service Value System, providing a holistic approach to the co-creation of value through service relationships.
Service value system
The service value system (SVS) is a key component of ITIL 4, which facilitates value co-creation. It describes how all the components and activities of an organization work together to enable value creation. As the SVS has interfa
ces with other organizations it forms an ecosystem and can also create value for those organizations, their customers and stakeholders.
At the heart of the SVS is the service value chain – a flexible operating model for the creation, delivery and continual improvement of services. The service value chain defines six key activities: plan; improve; engage; design and transition; obtain/build; and deliver and support. They can be combined in many different sequences, which means the service value chain allows an organization to define a number of variants of value streams, e.g. the v3 service lifecycle.
The four dimensions
A holistic approach to service management is key in ITIL 4.
The four dimensions are:
Organizations and people: An organization needs a culture that supports its objectives, and the right level of capacity and competency among its workforce.
Information and technology: In the SVS context, this includes the information and knowledge as well as the technologies required for the management of services.
Partners and suppliers: This refers to an organization’s relationships with those other businesses that are involved in the design, deployment, delivery, support, and continual improvement of services.
Value streams and processes: How the various parts of the organization work in an integrated and coordinated way is important to enable value creation through products and services
Guiding principles
ITIL 4 has seven guiding principles.
The ITIL 4 guiding principles are:
Focus on value
Start where you are
Progress iteratively with feedback
Collaborate and promote visibility
Think and work holistically
Keep it simple and practical
Optimize and automate
ITIL 4’s focus on collaboration, automation, and keeping things simple, reflect principles found in Agile, DevOps and Lean methodologies.
From processes to practices
ITIL has so far used “processes” to manage IT services.
This is known as “practices”, a fundamental part of the ITIL 4 framework. The SVS includes 34 management practices, which are sets of organizational resources for performing work or accomplishing an objective.
The ITIL practices share the same value and importance as the current ITIL processes but follow a more holistic approach.
The holistic approach
ITIL 4 puts service management in a strategic context. It looks at ITSM, Development, Operations, business relationships and governance holistically and brings the different functions together.
https://www.axelos.com/news/blogs/february-2019/from-v3-to-4-this-is-the-new-itil
- Machine learning is the key to AI adoption in ITSM
Machine Learning and ITSM
An example of a common use of machine learning in ITSM is the use of Chatbots or virtual assistants. While initially the goal is to program a bot with known questions and answers, there is also a significant focus on learning over time to respond to questions that have not been programmed previously based upon an attempt to understand the question’s intent.
ITSM and Automation
In ITSM, a vast amount of the work that is done to deliver and support services is repetative and is a likely candidate for automation. Teaching ITSM tools to look for patterns and learn from past events, incidents, problems, known errors
https://www.axelos.com/news/blogs/april-2019/machine-learning-is-the-key-to-ai-adoption-in-itsm
- ITIL 4 and cloud-based services
The first wave of change occurred with organizations outsourcing more and more IT infrastructure and applications to the cloud. Advantages often cited for this move include cost reduction, decreased IT asset ownership and reduced complexity of IT.
The second wave of change is happening with organizations contemplating the concept of digital transformation, and then embarking on a digital transformation journey.
how new structures in ITIL 4 relate to using cloud services. These include:
Impact of Cloud on IT Service Management & ITIL Lifecycle Processes
ITIL 4 updated for a digital world
Service Value System Considerations for Cloud
Service Value Chains. Adapted for Cloud
Value Stream Mapping
Service Financial Management
Service Level Agreements
DevOps, Change Control and Velocity of Change
It is worth remembering that the proliferation of cloud-based services does not change the fundamentals of what frameworks such as ITIL, or a movement such as IT service management, aim at. They want to achieve quality products and services which are fit for purpose, fit for use and aligned to the strategic goals and needs of the organization.
https://www.axelos.com/news/blogs/march-2019/itil-4-and-cloud-based-services
- ITIL 4 components
ITIL 4 consists of two key components:
The four dimensions model
The service value system (SVS).
ITIL 4 management practices
ITIL 4 includes 34 management practices as "sets of organizational resources designed for performing work or accomplishing an objective". For each practice, ITIL 4 provides various types of guidance, such as key terms and concepts, success factors, key activities, information objects, etc.
The 34 ITIL 4 practices are grouped into three categories:
General management practices
Service management practices
Technical management practices
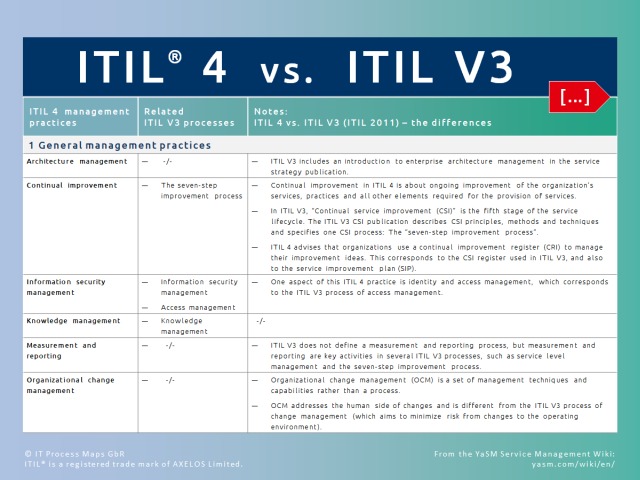
ITIL 4 and ITIL V3: What's the difference?
The service lifecycle has been dropped in ITIL 4 and the processes replaced with practices. But many of the ITIL 4 practices clearly correspond to the previous ITIL V3 processes.
ITIL 4 also provides advice for integrating ITIL with other frameworks and methodologies like DevOps, Lean and Agile.
https://wiki.en.it-processmaps.com/index.php/ITIL_4