- What Is a Security Service Edge (SSE)?
SSE is a collection of integrated, cloud-centric security capabilities that facilitates safe access to websites, software-as-a-service (SaaS) applications and private applications.
SSE-related security capabilities include Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA), cloud secure web gateway (SWG), cloud access security broker (CASB), and firewall-as-a-service (FWaaS) technologies.
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) is a category of technologies that provides secure remote access to applications and services based on defined access control policies. Unlike virtual private networks (VPNs), which grant complete access to a LAN, ZTNA solutions default to deny, providing only the access to services the user has been explicitly granted.
When looking at the full capability set that comprises a comprehensive SSE strategy, ZTNA provides a multi-layered, remote-access, security approach that provides redundant layers of inspection and enforcement, specifically:
Secure Web Gateway (SWG)
A secure web gateway (SWG) protects users from web-based threats in addition to applying and enforcing corporate acceptable use policies. Instead of connecting directly to a website, a user accesses the SWG, which is then responsible for connecting the user to the desired website and performing functions such as URL filtering, web visibility, malicious content inspection, web access controls and other security measures
SWGs are an important part of a comprehensive SSE strategy as they provide users secure internet access when they are disconnected from the business VPN
Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB)
CASBs help organizations discover where their data is across multiple software-as-a-service (SaaS) applications and when it’s in motion across cloud environments, on-prem data centers or accessed by mobile workers. A CASB also enforces an organization’s security, governance and compliance policies allowing authorized users to access and consume cloud resources while enabling organizations to effectively and consistently protect their data across multiple locations. There are two types of CASBs available: traditional CASBs and integrated CASBs.
An effective SSE strategy uses an integrated CASB to help organizations keep pace with the SaaS explosion.
Firewall-as-a-Service (FWaaS)
FWaaS enables firewalls to be delivered as part of a company’s cloud infrastructure to protect cloud-based data and applications.
An SSE strategy uses FWaaS capabilities to enable organizations to aggregate traffic from multiple sources – whether from on-site data centers, branch offices, mobile users or cloud infrastructure
https://www.paloaltonetworks.com/cyberpedia/what-is-security-service-edge-sse




- What is security service edge?
a convergence of network security services delivered from a purpose-built cloud platform.
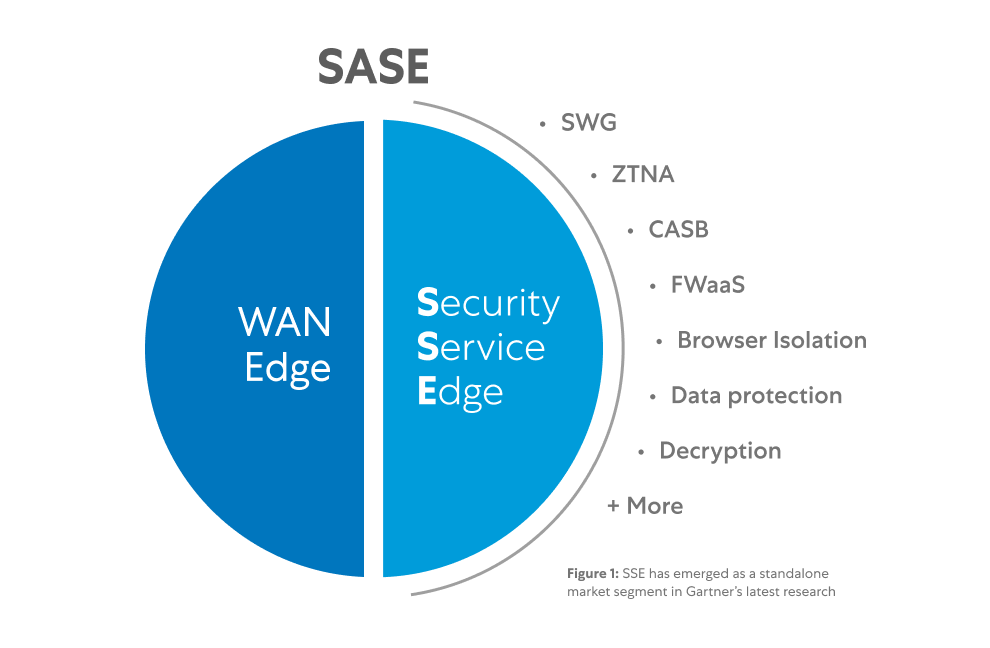
SSE can be considered a subset of the secure access service edge (SASE) framework with its architecture squarely focused on security services.
Secure access to the internet and web by way of a secure web gateway (SWG)
Secure access to SaaS and cloud apps via a cloud access security broker (CASB)
Secure remote access to private apps through zero trust network access (ZTNA)
What has driven the need for SSE?
As organizations adopt software and infrastructure as a service (SaaS, IaaS) offerings as well as other cloud apps, their data becomes more distributed outside their on-premises data centers. In addition, growing populations of users are mobile and remote, connecting from everywhere, over any connection, to their cloud apps and data.
Securing cloud apps and mobile users is difficult with traditional network security approaches because:
Anchored to the data center, legacy technologies can't follow connections between users and cloud apps.
Relaying ("hairpinning") user traffic to a data center via traditional VPN for inspection slows everything down.
VPNs are easy to exploit due to a lack of patching.
What's the difference between secure access service edge (SASE) and security service edge (SSE)?
You can look at a SASE platform in two slices. The SSE slice focuses on unifying all security services, including SWG, CASB, and ZTNA. The other, the WAN edge slice, focuses on doing so for networking services, including software-defined wide area networking (SD-WAN), WAN optimization, quality of service (QoS), and other means of improving routing to cloud apps.
Advantages of SSE over traditional network security
1. Better risk reduction
SSE also improves visibility across users—wherever they are—and data, regardless of the channels accessed
2. Zero trust access
SSE platforms (along with SASE) should enable least-privileged access from users to cloud or private apps with a strong zero trust policy based on four factors: user, device, application, and content.
3. User experience
4. Consolidation advantages
SSE can deliver many key security services—SWG, CASB, ZTNA, cloud firewall (FWaaS), cloud sandbox, cloud data loss prevention (DLP), cloud security posture management (CSPM), and cloud browser isolation (CBI)—all in one platform
Top SSE use cases
1. Secure access to cloud services and web usage
Enforcing policy control over user access to the internet, web, and cloud applications (historically performed by a SWG) is one of the primary use cases for the security service edge.Another key capability is cloud security posture management (CSPM), which protects your organization from risky misconfigurations that can lead to breaches.
2. Detect and mitigate threats
SSE platform must have advanced threat prevention capabilities, including cloud firewall (FWaaS), cloud sandbox, malware detection, and cloud browser isolation. CASBs enable inspection of data within SaaS apps and can identify and quarantine existing malware before it inflicts damage. Adaptive access control, whereby an end user's device posture is determined and access is adjusted accordingly, is also a key component.
3. Connect and secure remote workers
Providing secure access to private and cloud apps without needing to open firewall ACLs or expose apps to the internet is key here. SSE platforms should enable native inside-out app connectivity, keeping apps "dark" to the internet
4. Identify and protect sensitive data
Cloud DLP enables sensitive data (e.g., personally identifiable information [PII]) to be easily found, classified, and secured to support Payment Card Industry (PCI) standards and other compliance policies. SSE also simplifies data protection, as you can create DLP policies just once and apply them across inline traffic and data at rest in cloud apps via CASBs.
The most effective SSE platforms also deliver high-performance TLS/SSL inspection to address encrypted traffic (that is, most data in transit). Also key for this use case is shadow IT discovery, which allows organizations to block risky or sanctioned applications across all endpoints.
https://www.zscaler.com/resources/security-terms-glossary/what-is-security-service-edge
- sase is combination of network as a service and security as a service capabilities.
sase is delivered as a service business model to the cloud.
Thin Edge Users -> application aaS + data center + SaaS + IaaS + Internet -> Remote Off-Network Users
Secure Access Service Edge(SASE) vs VPN-only
Network as a Service + Security as a Service -> SASE
Network as a Service -> Peering - > Direct network connection and traffic exchange across the internet
Security as a Service -> NGFW or cloud-based Firewall as a Service
NGFW or cloud-based Firewall as a Service - > Physical Device or cloud-based
Full stack security
IPS
Anti-Malware
SSL Inspection
Sandbox
Secure Web Gateway - > Filter Malware
Enforce internet security and compliance policies
Zero Trust Network Access(ZTNA) - > Identify users and devices and authenticate and authorize
Technologies
Multi-Factor Authentication(MFA)
Network Access Control(NAC)
Access Policy Enforcement
Data Loss Prevention(DLP) - > Prevents moving key information outside the network authorize
Informs content inspection of messaging and email applications
Domain Name System(DNS) - > Informs SASE with detailed threat detection capabilities
Analyze and assess risky domains
https://training.fortinet.com/pluginfile.php/1622279/mod_scorm/content/1/story_content/external_files/NSE%202%20SASE%20Script_EN.pdf




