- How To use an SPF Record to Prevent Spoofing & Improve E-mail Reliability
A carefully tailored SPF record will reduce the likelihood of your domain name getting fraudulently spoofed and keep your messages from getting flagged as spam before they reach your recipients.
Email spoofing is the creation of email messages with a forged sender address; something
Spam and phishing emails typically use such spoofing to mislead the recipient about the origin of the message.
SPF,
Sender ID,
DKIM,
and DMARC.
Sender Policy Framework (SPF) is an email validation system designed to prevent spam by detecting email spoofing.
Today, nearly all abusive e-mail messages carry fake sender addresses. The victims whose addresses are being abused often suffer from the consequences, because their reputation gets diminished, they have to waste their time sorting out misdirected bounce messages, or (worse) their IP addresses get blacklisted.
The SPF is an open standard specifying a technical method to prevent sender-address forgery.
SPF allows administrators to specify
Benefits
Adding an SPF record to your DNS zone file is the best way to stop spammers from spoofing your domain. In addition, an SPF Record will reduce the number of legitimate e-mail messages that
The SPF record is not 100% effective, unfortunately, because not all mail providers check for it
Although you do not need an SPF record on your DNS server to
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/how-to-use-an-spf-record-to-prevent-spoofing-improve-e-mail-reliability
- What is SPF?
SPF is an email authentication mechanism which allows only
your business domain is
your email delivery server, which
some attacker uses a scam email server at IP address 1.2.3.4 to
When an email delivery service connects to the email server serving up the recipient's mailbox:
the email server extracts the domain name from the envelope from address;
the email server checks the connecting host's IP address to see if it's listed in
For example, let's say your SPF record looks like this:
v=spf1 ip4:192.168.0.1 -all
it means only emails from IP address 192.168.0.1 can pass SPF check, while all emails from any IP address other than 192.168.0.1 will fail. Therefore, no email from the
What is DKIM?
One important aspect of email security is the authenticity of the message. An email message usually goes through multiple
DKIM, which stands for
DKIM enables the receiver to check if email headers and content have
Asymmetric cryptography
One of the best-known uses of asymmetric cryptography is digital signatures, in which a message
How DKIM works
On a high level, DKIM authentication
create a
keep the private key with the signing server;
publish the public key to the DNS in a DKIM record, so that the verification server has access to it.
What is DMARC?
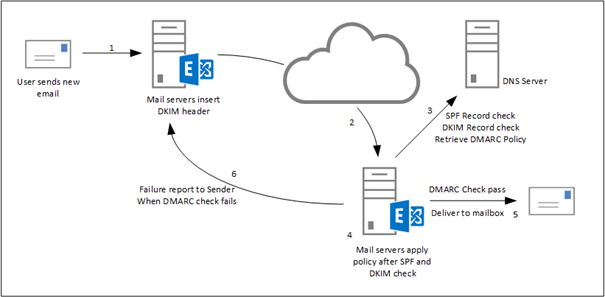
DMARC, which stands for Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance, is a way to determine whether an email message is actually from the sender or not. It builds on the widely deployed SPF and DKIM protocols, and adds domain alignment checking and reporting capabilities to designated recipients, to improve and monitor the protection of the domain against nefarious spoofing attempts
How DMARC works
On a high level,
Here is how DMARC works: first you publish a DMARC record for your email domain in the DNS; whenever an email that claims to have originated from your domain
DMARC implements identifier alignment to eliminate the discrepancy between envelope from/header from addresses in SPF, and that between d= value and header from
DMARC adds reporting capabilities to enable email domain owners to gain visibility into email
DMARC alignment: authentication hardened
When either of the following is true of an email message, we say the email is DMARC aligned:
it passes SPF authentication, and SPF has identifier alignment;
it passes DKIM authentication, and DKIM has identifier alignment.
https://dmarcly.com/blog/home/how-to-implement-dmarc-dkim-spf-to-stop-email-spoofing-phishing-the-definitive-guide#introduction-to-spf
- SPF is using an SPF record in public DNS
where all legitimate outbound SMTP servers for a domain are listed . A receiving SMTP server can check this DNS record to make surethe sending mail server is allowed to send email messages on behalf of the user or his organization
DKIM is about signing and verifying header information in email messages. A sending mail server can digitally sign messages, using a private key that’s only available to the sending mail server. The receiving mail server checks the public key in DNS to verify the signed information in the email message. Since the private key is only available to the sending organization’s mail servers, the receiving mail server knows that it’s a legitimate mail server, and thus a legitimate email message.
DMARC or Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance
DMARC which stands for Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance is an email validation mechanism, built on top of SPF and DKIM. DMARC is using a policy
https://jaapwesselius.com/2016/08/23/senderid-spf-dkim-and-dmarc-in-exchange-2016-part-iii/