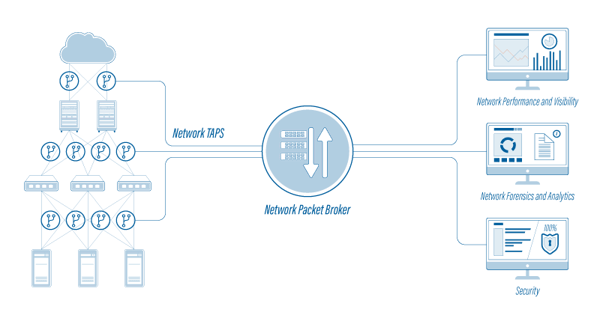
- What Is a Network Packet Broker?
What is a network packet broker (NPB)? A network packet broker is a technology that implements a range of monitoring tools to access and analyze traffic (also known as “network packets”) across a network. Simply put, NPBs function as ‘brokers’ (or managers) of network traffic. The packet broker collects traffic from multiple network links, filtering and distributing each individual packet to the correct network monitoring tool. By doing so, network packet brokers ensure improved effectiveness from network monitoring and security tools, by delivering improved data from across the network
https://www.gigamon.com/campaigns/next-generation-network-packet-broker.html
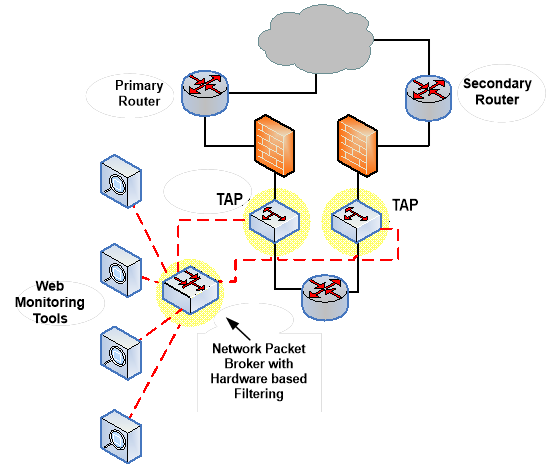
- To avoid waste and blind spots, start by collecting data about what is taking place across
your network. Network taps and mirror ports on network equipment—also known as
switched port analyzer or SPAN ports—create access points for capturing traffic for analysis.
Why Do I Need a Network Packet Broker?
A Network Packet Broker (NPB) resides between taps and SPAN ports. They can access
network data and sophisticated security and monitoring tools that typically reside in data
centers. NPB’s do just what their name says: they broker network packet data to ensure every
analysis tool sees exactly the data it needs to perform at the highest possible level. The NPB
adds an increasingly critical layer of intelligence—one that reduces cost and complexity to help
you achieve the following:
Faster problem resolution
e. Ixia’s robust Security Fabric
leverages this intelligence to speed up troubleshooting by providing insight into the geographic
location of outages and the vendors that may be causing disruptions
Increased proactivity
The use of metadata, provided through NetFlow by intelligent NPBs, also aids
in accessing the empirical data used to manage bandwidth usage, trending,
and growth. That prevents problems from occurring in the first place.
What Exactly Does the NPB Do?
Conceptually, aggregating, filtering, and delivering data sounds simple
One way they do this is by load balancing traffic. For example, if you upgrade your data
center network from 1Gbps to 10Gbps, 40Gbps, or higher, NPBs can downshift speeds. That
allows you to distribute higher speed traffic across a pool of existing lower-speed 1G or 2G
monitoring tools for analysis.
Deduplicating redundant packets
Analysis and security tools stand to receive a slew of duplicate packets as multiple taps
forward traffic. NPBs can eliminate duplicates to keep tools from wasting processing capacity
by handling redundant data
SSL decryption
Secure Socket Layer (SSL) encryption is the standard technology used to safely send private
information. However, hackers can hide cyberthreats in encrypted packets.
Decryption is necessary to inspect this data, but unraveling code takes valuable processing
power. Leading packet brokers can offload decryption from security tools to ensure total
visibility while easing the burden on high-cost resources
Data masking
SSL decryption leaves data visible to anyone with access to security and monitoring tools.
NPBs can mask personally identifiable information such as credit card and Social Security
numbers, protected health information, and other sensitive data, before passing it on. That
means tools and their administrators cannot see it.
Protocol header stripping
An NPB may strip out protocol headers such as VLAN, VXLAN, and L3VPN, allowing tools that
process these protocols to receive and process packet data. Context-aware visibility helps
in spotting rogue applications running on your network and footprints attackers leave as they
work their way through your systems and networks.
https://www.keysight.com/us/en/assets/3120-1272/brochures/What-Is-a-Network-Packet-Broker-And-Why-Do-You-Need-One.pdf