- Continuous Integration solution for Windows and Linux. Build, test, deploy your apps faster, on any platform.
- Travis CI
https://travis-ci.org
- What is Travis CI?
Usually
What does it do?
Travis sets up “hooks” with GitHub
the free version of Travis to set up tests that run every time you try to merge new changes into that repo.
https://www.raywenderlich.com/1618-travis-ci-tutorial-getting-started
- Whether you need the simplicity of a cloud-hosted solution or the control of hosting on your own private infrastructure
Automate your development process quickly, safely, and at scale.
https://circleci.com/
- Bringing back the joy of iOS & Android development through automating build, testing and support cycles
https://www.bitrise.io/
- How to make CI, CT and CD work together and avoid the drama of a DevOps love triangle
Continuous Integration (CI) is
CI puts a great emphasis on testing automation to check that the application
Committing code triggers an automated build system to grab the latest code from the shared repository and to build, test and validate the full master branch.
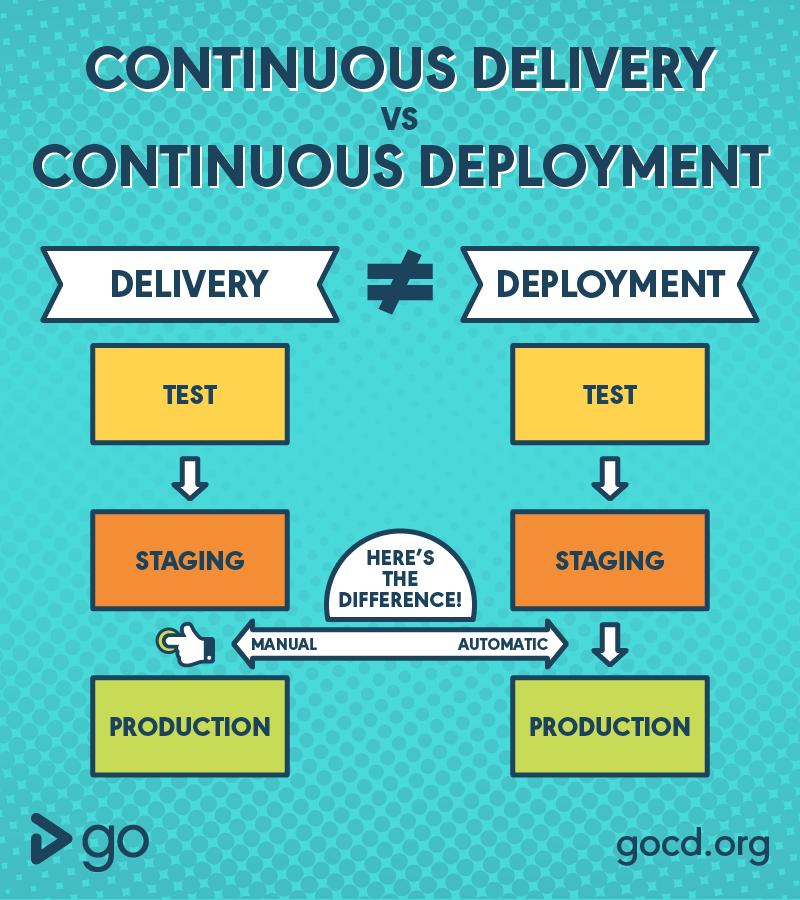
Method #2: Continuous Delivery
Continuous Delivery (CD) is the practice is the practice of streamlining and automating all the processes leading up to deployment. There are
Teams should ensure they have a monitoring dashboard for your production environment in place
Method #3: Continuous Testing
Continuous Testing (CT), which can also
The first, is perhaps the most obvious - communication.
It allows teams to be Agile by ensuring they are all on the same page, so if they leave a project or move on to a different step
The second is trust
By eliminating the element of doubt, teams can trust both the process and the product - assured that continuous quality is being prioritised.
https://www.itproportal.com/features/how-to-make-ci-ct-and-cd-work-together-and-avoid-the-drama-of-a-devops-love-triangle/
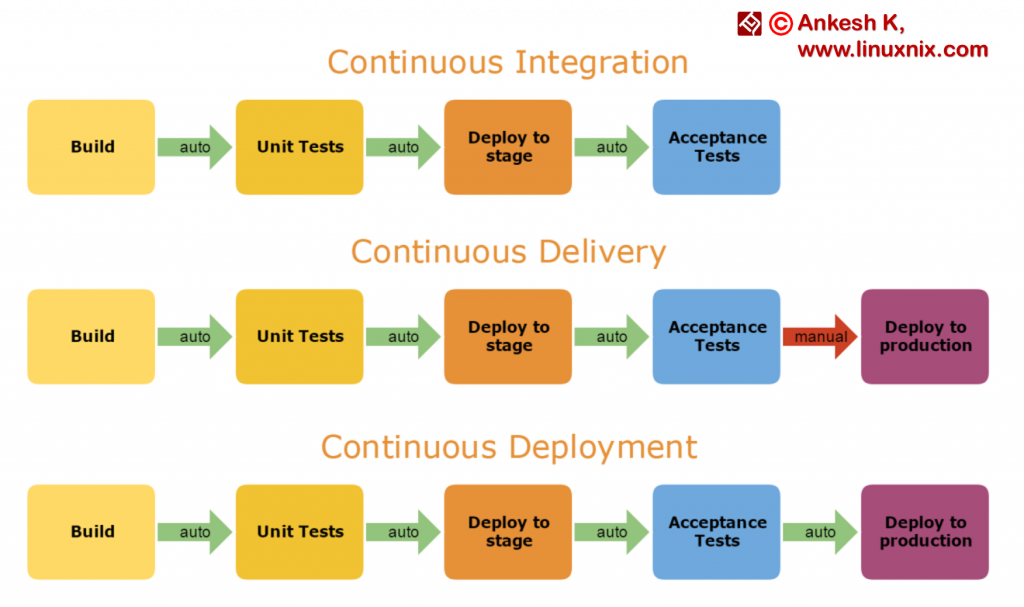
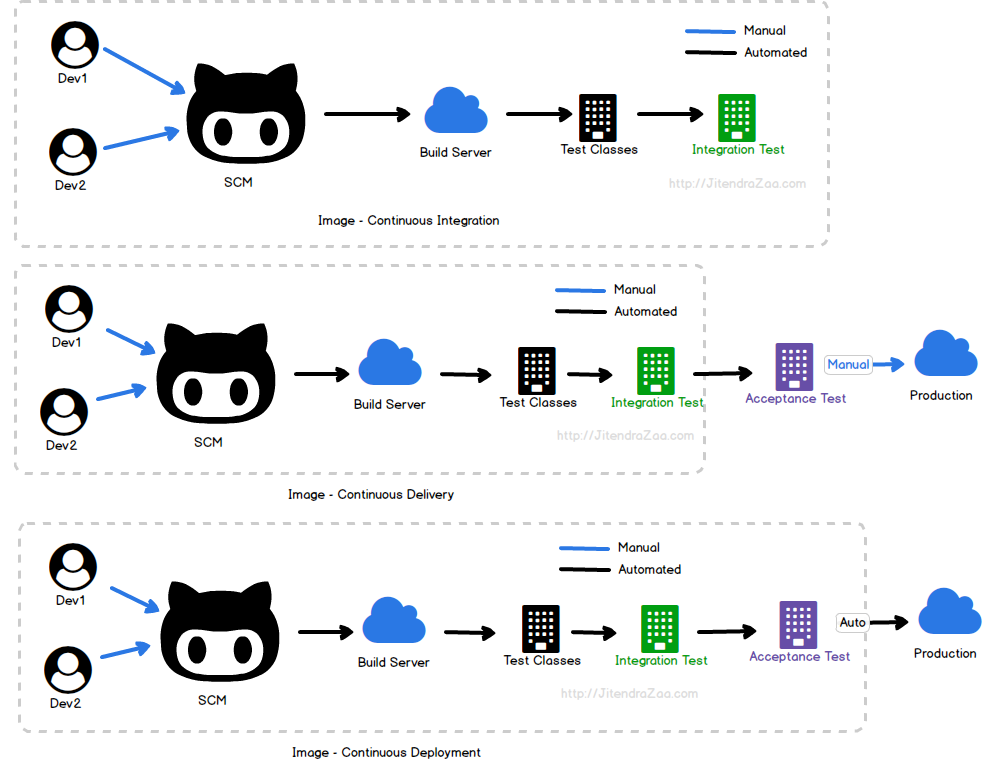
- What is Continuous Integration, Delivery, Deployment and CI-CD Pipeline
?
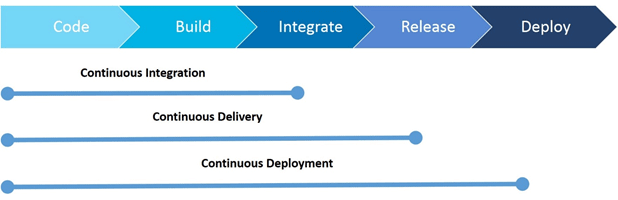
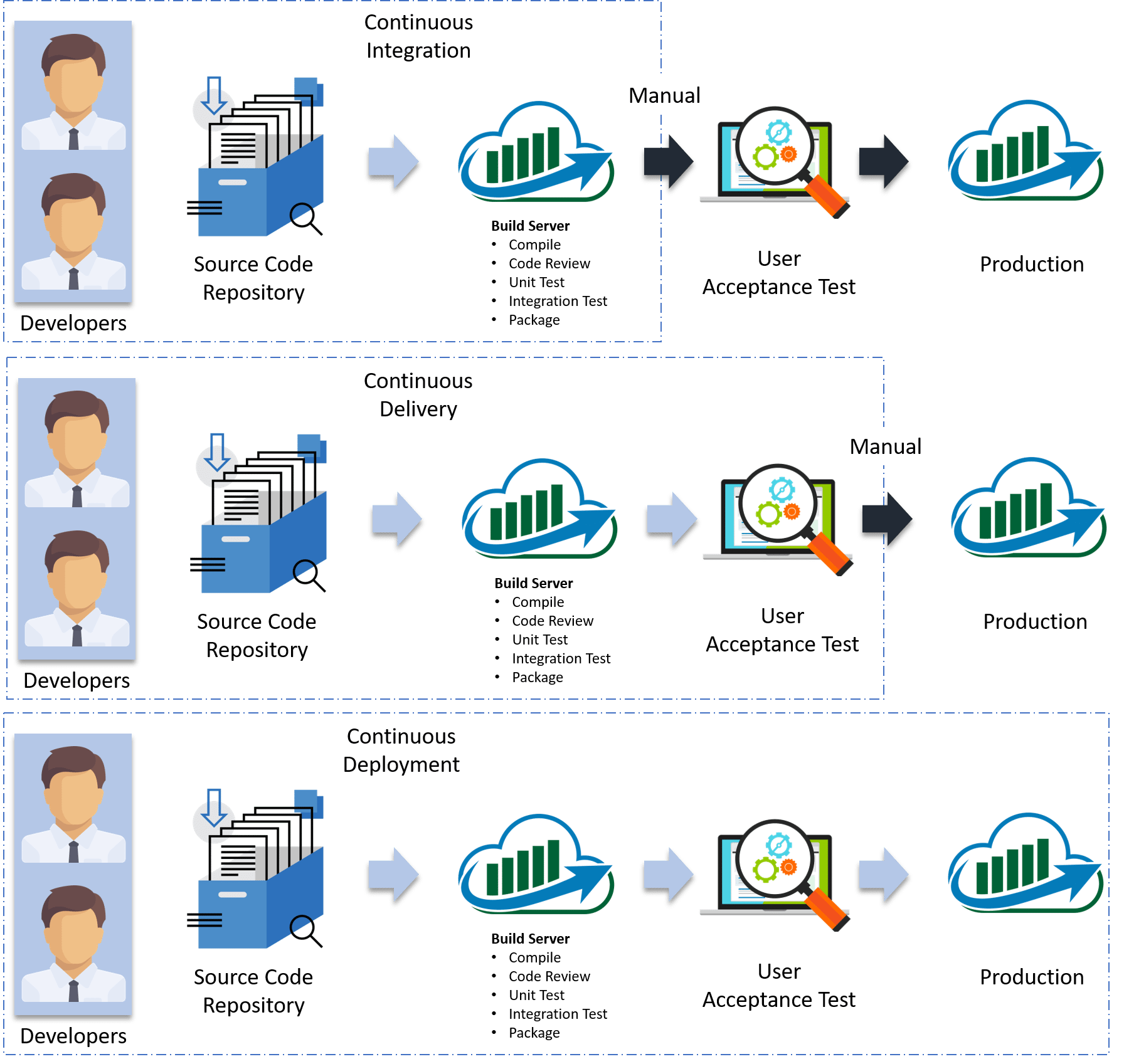
What is Continuous Integration?
Continuous Integration (CI) is a DevOps development practice which requires developers to push code into a central hub (also known as Source Code Management System) several times a day. Each commit
What is Continuous Testing?
Continuous Testing (CT) ensures that every time an integration
What is Continuous Deployment?
Continuous Deployment (CD) is the deployment process where you deliver software in a continuous incremental fashion and deploy frequently. Here the deployment could be in any environment in an automated way (DTAP
What is Continuous Delivery?
Continuous delivery is the practice of keeping your code deployable at any point. This process makes sure the build passes all the tests and be ready to push to the production at any moment of time
Continuous Workflow Overview
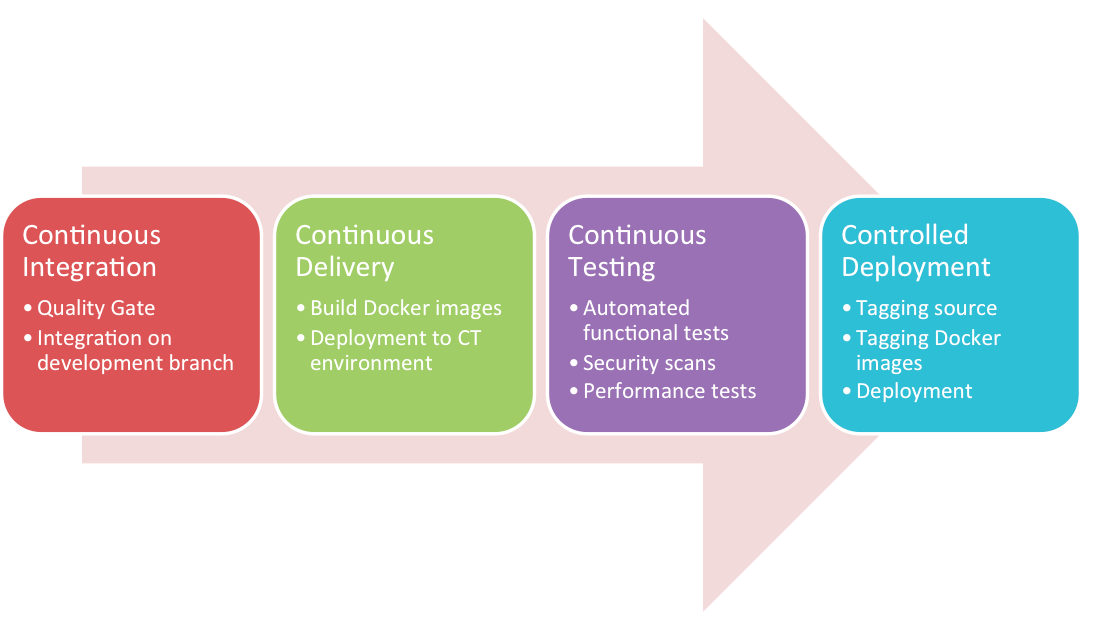
For any process to be continuous, there must be CI, CT, and CD incorporated in the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC).
Continuous Deployment and Continuous Delivery have become the best-practice in the industry for keeping your application deployable at any moment of time and pushing the code into production whenever a new change
https://www.linuxnix.com/what-is-continuous-integration-delivery-deployment-and-ci-cd-pipeline/
- Continuous everything in DevOps
…
the main practices are the same and the difference is mainly in where to apply automation. In Continuous Delivery, you aim to have the full software delivery life cycle automated
https://www.accenture.com/us-en/blogs/blogs-continuous-everything-devops
- Adding the “Continuous” to Integration
Continuous Integration is essentially the repetition of the integration step with a high frequency to
When a team practices Continuous Integration…
Developers are not working in isolation.
Testing happens automatically both at the feature level and at the mainline level.
Adding the “Continuous” to Delivery
Continuous Delivery is the practice of packaging and preparing the software (as if it
After
Deployments were happening
Releases create tension between developers (who want to ship new features) and operations (who want stability and don’t want to deploy too many new features at once).
each new feature is a potential candidate for pushing to production
Not all candidates
The human only decides if a release is going to production or not
The release
Continuous Delivery is
Builds should be repeatable and deterministic.
All configuration and associated files should exist in source control (not just source code).
Each
All test suites should
Once CD is in place, releases become trivial as
the release
Any project stakeholder should be able to give the green light and move the release to production immediately.
Release candidates that don’t reach production
Bonus: Continuous Deployment
The “D” in CD can also mean Deployment. This development approach builds upon Continuous Delivery and essentially completely removes all human intervention
https://thenewstack.io/understanding-the-difference-between-ci-and-cd/
- deterministic
In mathematics, computer science and physics, a deterministic system is a system in which
https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki ›
- In general,
idempotence be applied result in idempotency you can be sure
https://shadow-soft.com/ansible-idempotency-configuration-drift/
How to build an efficient CI/CD pipeline
DevOps Summit 2015 Presentation: Continuous Testing At the Speed of DevOps
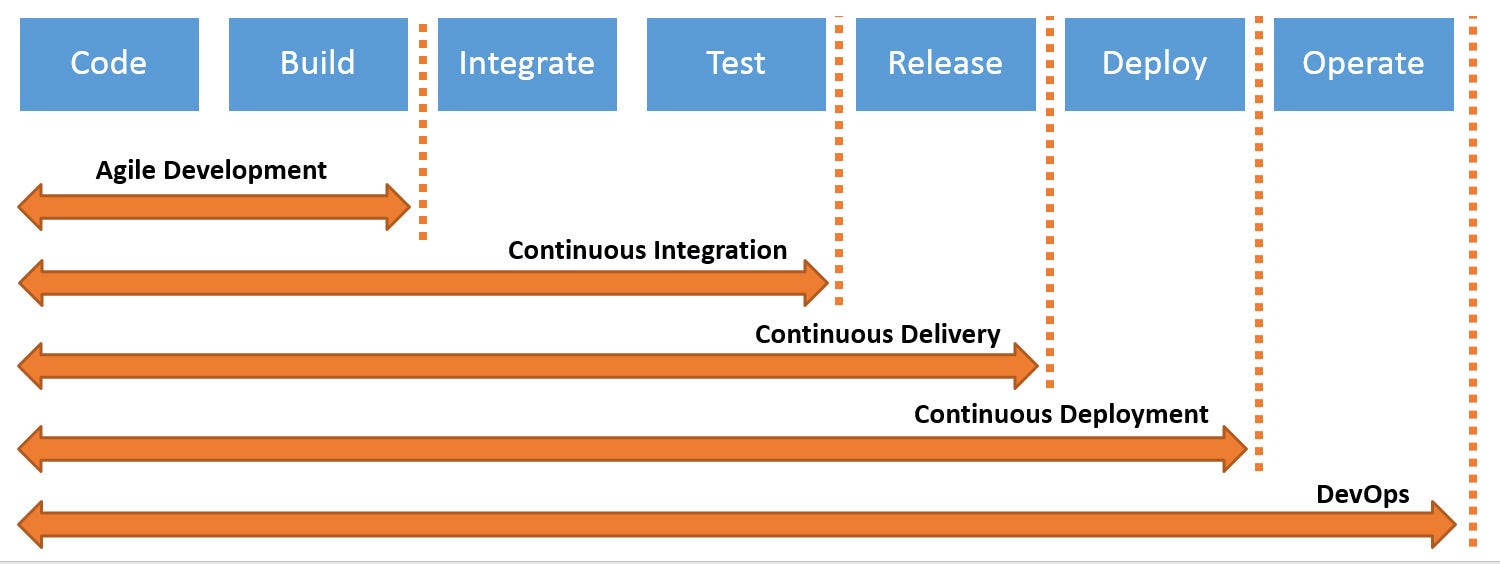
Continuous Delivery vs Deployment vs Integration: What’s the Difference?
- Continuous Delivery vs Deployment vs Integration: What’s the Difference?
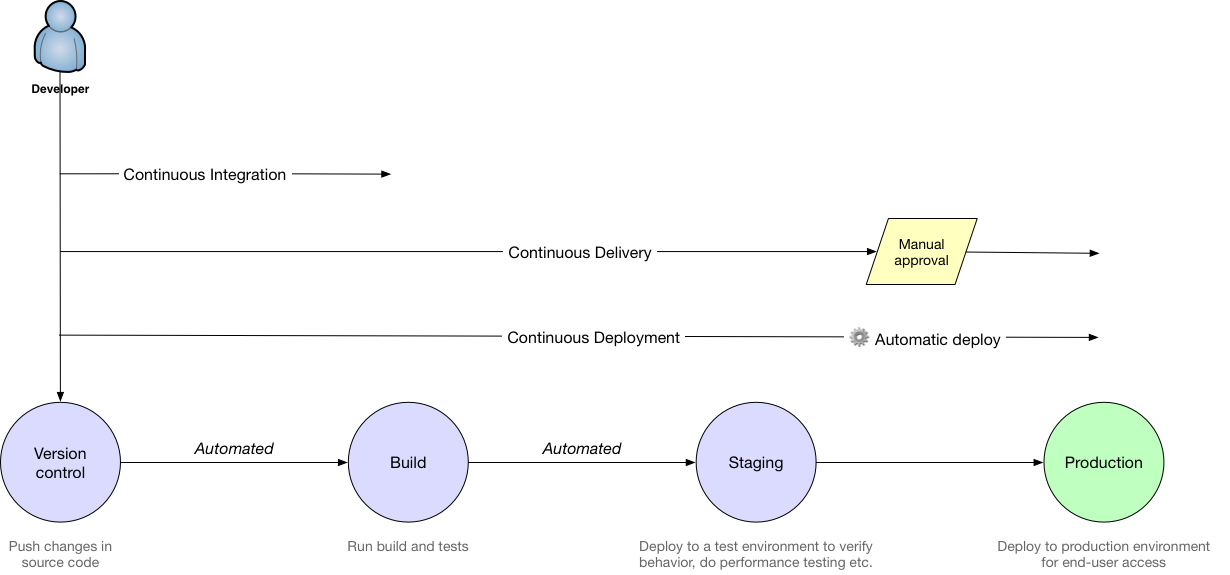
The ideal process would look like the following
The developer submits the code to the development branch.
The continuous integration servers picks up the change,
The developer deploys the code to the staging environment where QA tests the environment.
https://www.bmc.com/blogs/continuous-delivery-continuous-deployment-continuous-integration-whats-difference/
- Continuous… Integration. Delivery. Deployment.
Continuous Delivery
Continuous Delivery (CD) is a software development practice in which continuous integration, automated testing, and automated deployment capabilities allow high-quality software to be developed
Continuous Deployment
Continuous Deployment is a software development practice in which every code change goes through the entire pipeline and is put
With Continuous Delivery your software is always release any updated working version of the application is automatically pushed
Continuous Deployment mandates Continuous Delivery, but the opposite is not required
https://www.cloudbees.com/resources/continuous-delivery-101/continuous-deployment
What’s the Difference Between Continuous Integration, Continuous Deployment and Continuous Delivery?
Continuous Integration, Delivery, and Deployment Differentiated
- What is Continuous Delivery (CD)?
With CDE, the code is compiled
With this methodology be held are added be released methodology
Release Control
With a product that’s always production ready, the deployment to production becomes a business decision, providing total control over the user experience
Additional Testing
This model allows the production-ready product to undergo additional, more comprehensive testing in various test environments, including integration testing, system integration testing (SIT), User Acceptance Tests (UAT), load testing, performance testing, and any others that your organization may require
What is Continuous Deployment (CD)?
continuous deployment (CD) enables a development team to integrate code segments to the production environment several times per day. This methodology
Some perceive it as taking control of when to move code to production from the leadership and giving it to the developers.
Enhanced Delivery Velocity
With continuous deployment, the developer can check code and get a pass/fail notification within minutes. If an issue is detected no issues are detected the new code is moved automatically
Shift Left
When a developer checks in code, the automated processes take the code and move it through the entire lifecycle an issue is detected is notified
Real World Experimentation
This model also allows for real-world experimentation, such as A/B testing, and allows for immediate consumer feedback. For example, if you need to change the location of a certain feature on a website, but you’re not sure of the best new location, you could make the change, monitor real-time customer usage, and make adjustments accordingly.
https://www.plutora.com/blog/continuous-integration-continuous-delivery-continuous-deployment
- Continuous deployment vs. continuous delivery
Continuous deployment can be part of a continuous delivery pipeline. Specifically, continuous delivery is the automated movement of code through the development lifecycle (sometimes called the delivery lifecycle ); continuous deployment is the automated movement of that code into production, once it passes the required automated tests.
Whether you make continuous deployment part of your delivery pipeline depends on your business needs. If the business needs the delivery team to release new or updated software out to production repeatedly, reliably, or as quickly as possible, or if the solution has multiple dependencies, then it is likely you will benefit from continuous deployment.
https://www.ibm.com/cloud/learn/continuous-delivery