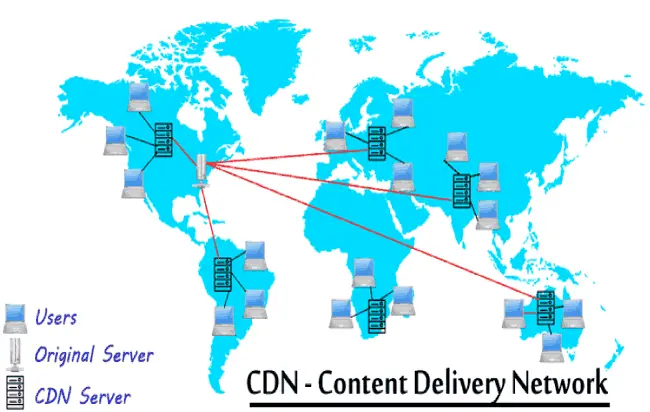
- A content delivery network or content distribution network (CDN) is a system of computers containing copies of data placed at various nodes of a network. When properly designed and implemented, a CDN can improve access to the data it
caches
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Content_delivery_network
- Akamai
http://www.akamai.com/
- limelight
- Bypassing the CDN protection
In this article, you
Many users use a CDN to shield their servers against
You need to know that the CDN supports protocols like HTTP and HTTPS, so if you have any other services like SSH or FTP, they will
An attacker will need to know the IP if they want to access to any of
1. Subdomains
By using online tools like
If you check them, you will find two ways to discover the IP.
The first one
ftp
smtp
dns
1.1
If you want to find more
Once you have
The second way, you need to check all the IP’s which are pointing to the
2. DNS track
Your servers might
3. IOT Tools
3.1. Shodan
the
3.2. Censys
it has a historical section where past results
3.3. Zoom Eye
4. Email headlines
Checking email headlines is another way to find the IP of a server.
https://opendatasecurity.io/how-to-bypass-cdn/
- What is CloudFlare? What does CloudFlare do with my website after I activate my website on CloudFlare?
CloudFlare is a Content Delivery Network which builds up a wall between the website and the visitor. Only visitors are allowed to are allowed ( . . .
https://theshadowpress.com/configuring-cloudflare-website-to-avoid-getting-it-bypassed/
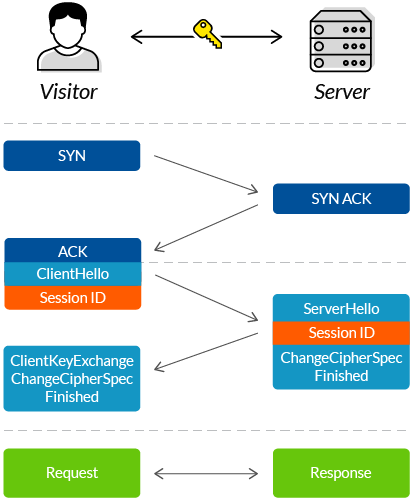
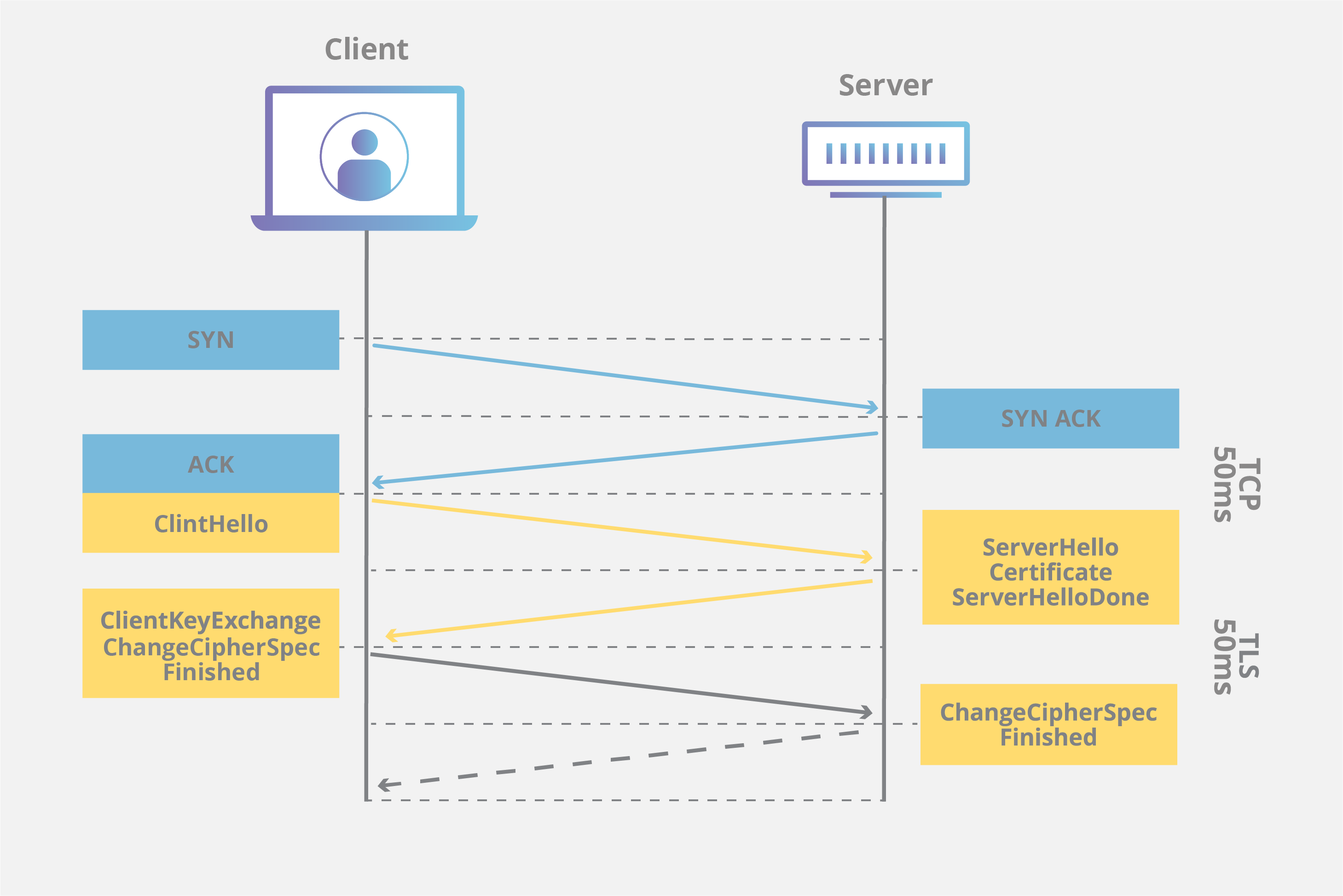
A typical TCP connection is established
Agree upon a mutually-compatible
Go through a process of mutual verification.
Generate symmetric keys, used to encode and decode all information exchanged during the session.
These extra interactions add overhead to the process, resulting in two additional round trips—or more, depending on your server’s configuration.
Solution:
Use a CDN to Reduce Round Trip Time
Shortening round trip time is a core function of CDN—a service specifically designed to improve response speeds by reducing the physical distance between your website and its users.
What is a CDN
Content delivery networks (CDN) are the transparent backbone of the Internet in charge of content delivery.
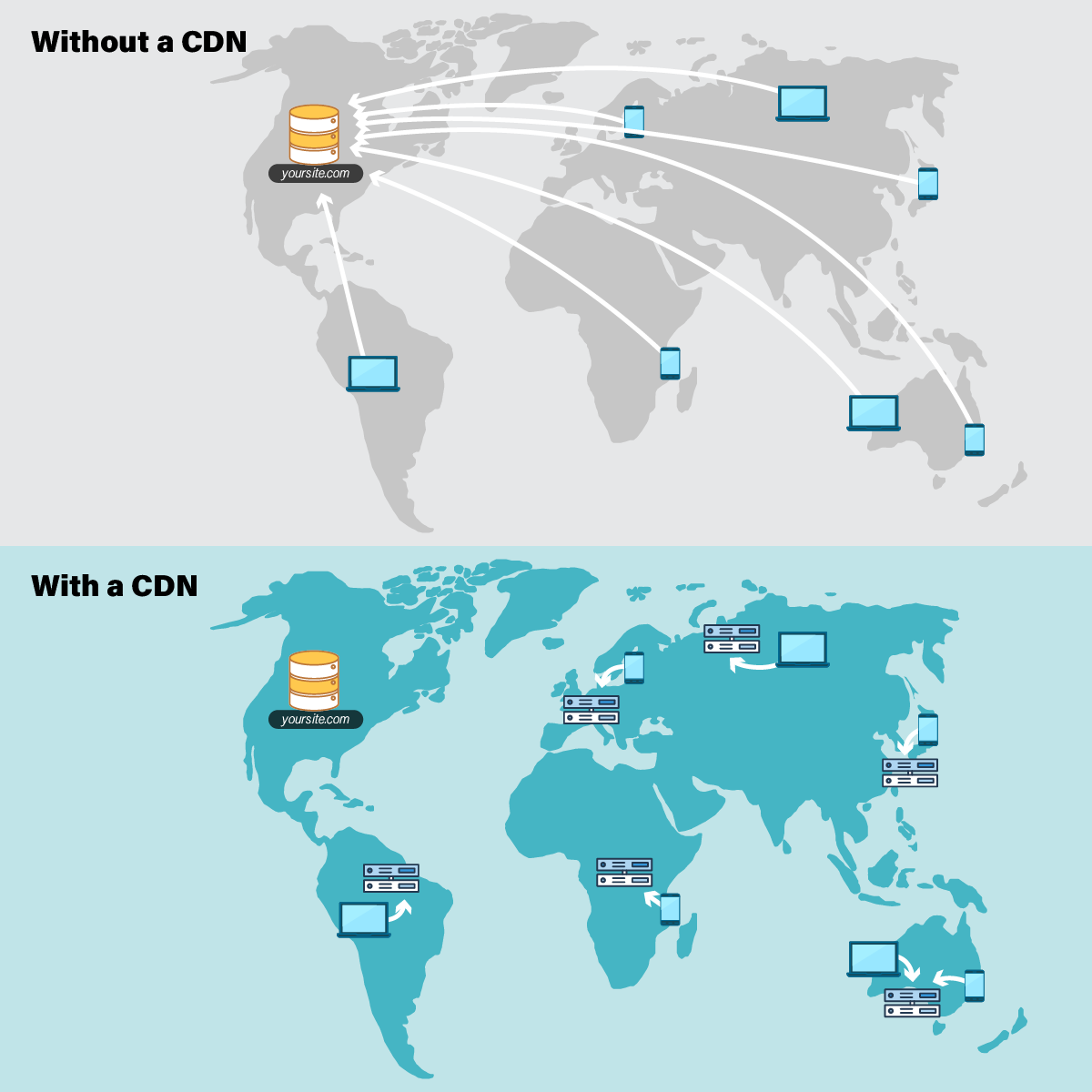
To understand why CDNs are so widely used, you first need to recognize the issue they’re designed to actually onscreen
In all cases however, the delay duration is impacted
A CDN’s mission is to virtually shorten
points of presence, or PoPs
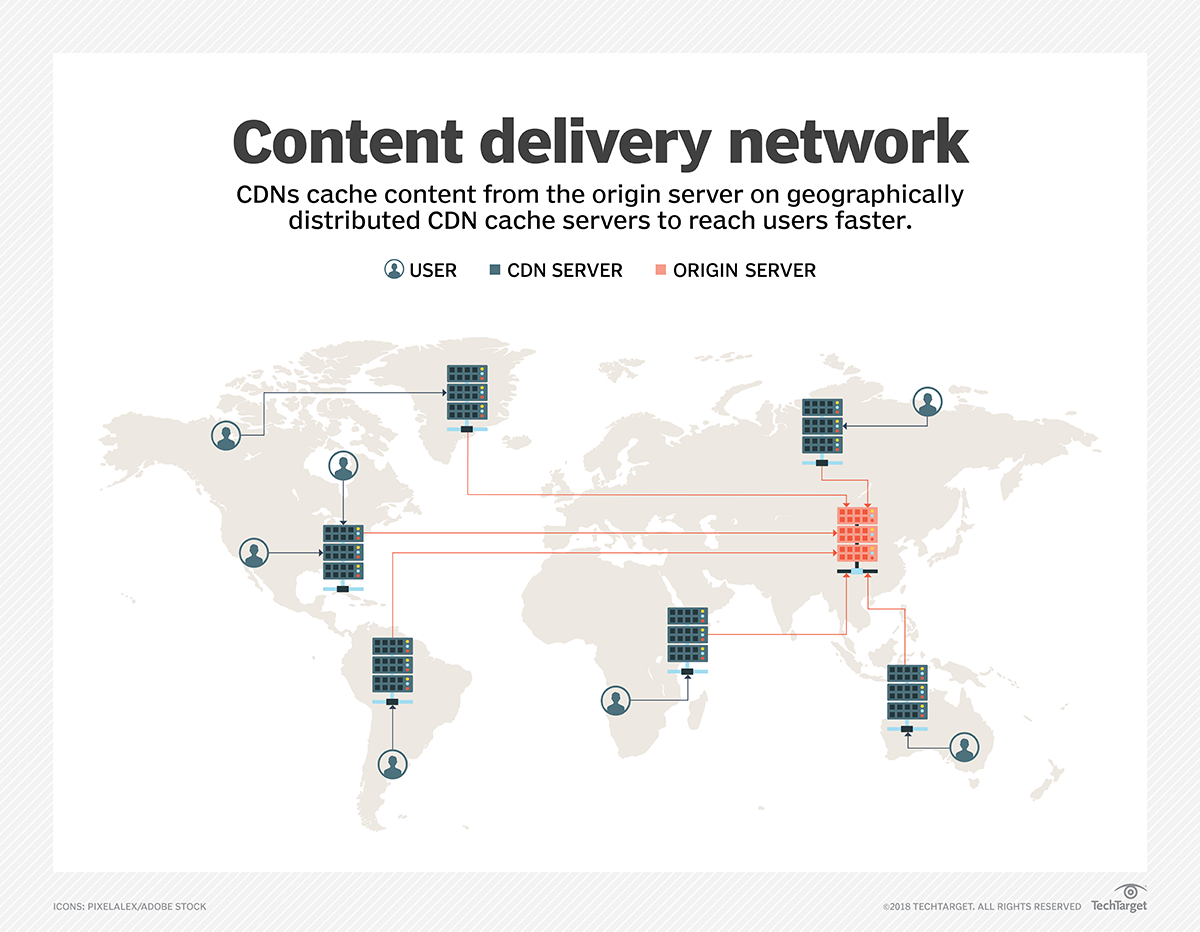
How a CDN Works
To minimize the distance between the visitors and your website’s server, a CDN stores a cached version of its content in multiple geographical locations (a. . a number of
For example, when someone in London accesses your US-hosted website, it is done
Specifically, if you are running a strictly localized website, with the vast majority of your users located actually
CDN BUILDING BLOCKS
PoPs(
CDN PoPs (Points of Presence) are strategically located numerous
Caching Servers
Each CDN caching server typically holds multiple storage drives and high amounts of RAM resources.
SSD/HDD + RAM
Inside CDN caching servers, cached files are stored commonly-used
START USING A CDN
For a CDN to work, it needs to be the default inbound gateway for all incoming traffic. To make this happen, you’ll need to modify subdomains . img .
For your root domain, you’ll change its subdomain modify subdomain . cdn
START USING A CDN
For a CDN to work, it needs to be the default inbound gateway for all incoming traffic. To make this happen, you’ll need to modify subdomains . img .
For your root domain, you’ll change its subdomain modify subdomain . cdn
Why isn’t a CDN a Default Part of my Website Hosting?
In an ideal world, a CDN would be an integral part of any website hosting. However, when CDNs were first established in the late 1990s, they were far too expensive and only accessible to the largest organizations.
THE EVOLUTION OF CDNs
1st Gen Static CDN
2nd Gen Dynamic CDN
3rd Gen Multi-Purpose CDN
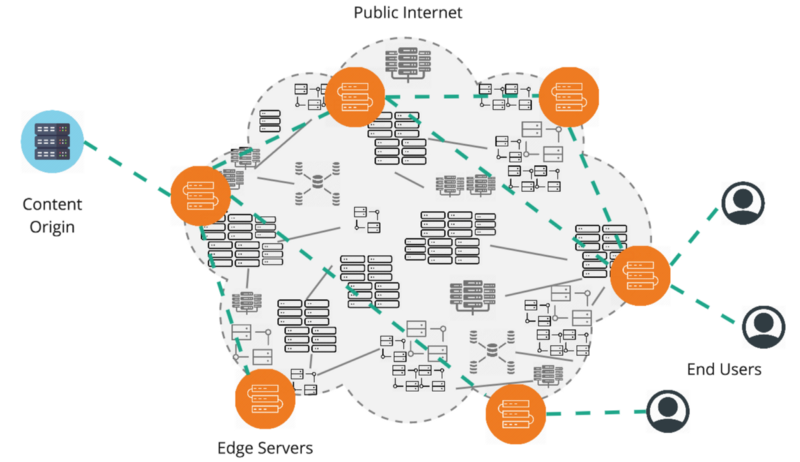
REVERSE PROXY LIVING ON THE EDGE
Content delivery networks employ CDNs are deployed (
the reverse proxy topology is being leveraged by multi-purpose CDNs to provide the following types of
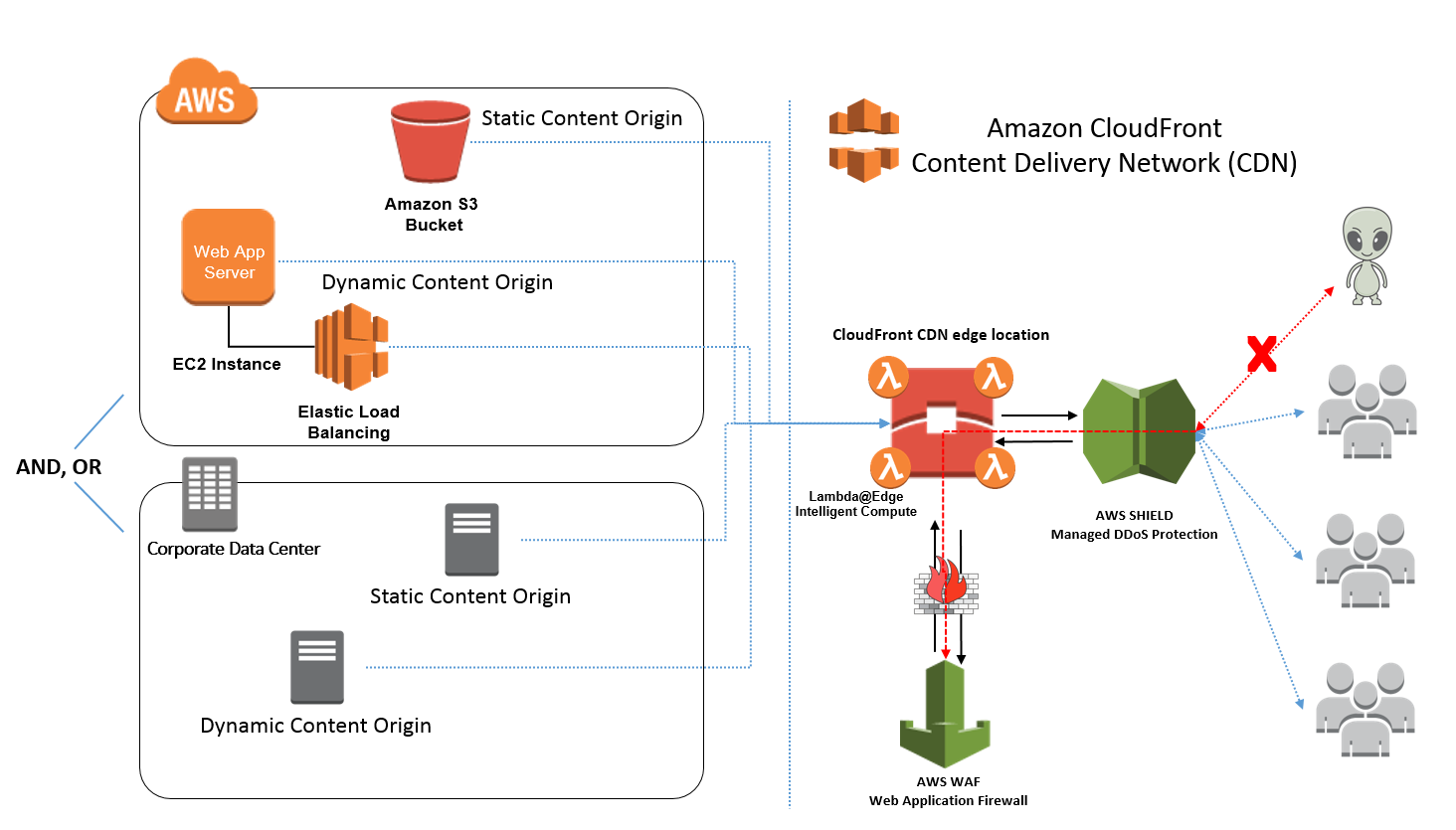
Website Security
Deployed on the edge of your network, a CDN is perfectly situated DDoS
Load Balancing
Load balancing is all about having a “traffic guard” positioned in front of your servers, alternating the flow of incoming requests in such a way that traffic jams are avoided
https://www.imperva.com/learn/performance/what-is-cdn-how-it-works/
- As of 2015, the last version of SSL (3.0)
was officially deprecated been replaced simply
How A CDN Can BOLSTER SSL/TLS PERFORMANCE
let’s first review how an SSL connection differs from it regular TCP counterpart.
the time it takes
negotiating a SSL forths
This is because the browser and server now also need to:
Agree upon a mutually-compatible
Go through a process of mutual verification.
Generate symmetric keys, used to encode and decode all information exchanged during the session.
These extra interactions add overhead to the process, resulting in two additional round trips
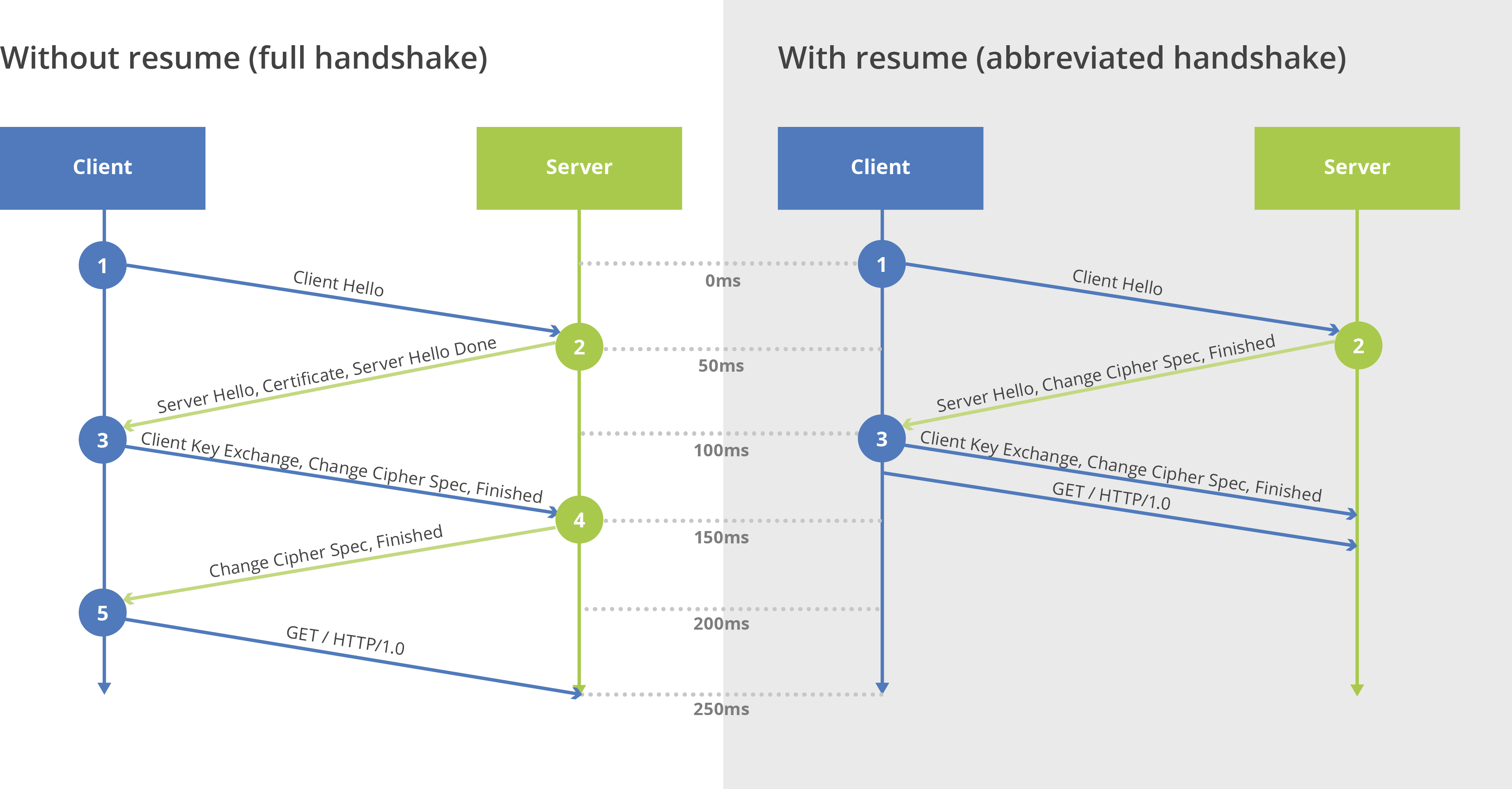
For example
If the round trip time from San Francisco to your London server is 50 ms, then establishing a SSL
Solution:
Use A CDN To Reduce Round Trip Time
Shortening round trip time is a core function of CDN—a service specifically designed to improve response speeds by reducing the physical distance between your website and its users.
CDN also speeds up all interactions during the SSL/TLS negotiation process
What is important here is to ensure that your CDN has a keep-alive functionality, also referred to as a persistent connection.
For example
After the SSL connection with the LA proxy is established
The round trip time between LA and London is 30 ms, so it will take 90 ms to negotiate the second SSL connection. This brings the total handshake time back to 150 ms.
some server configurations can accelerate
False Start Enables the browser to send encrypted application data even before the SSL negotiation is complete.
Session Resumption Caches a visitor’s and server’s information to reduce negotiation times for repeat visitors.
SL/TLS communications rely on the existence of SSL certificates. These contain information about your domain and organization, in addition to initiate
there is a difference between those SSL certificates purchased from an official certificate authority (CA), and free (self-signed) ones that can be generated
a CA certificate is clearly
all SSL/TLS certificates are graded
Protocol support – is given
Cipher support – is given
CDN For An No
Using a CDN means that the first leg of your SSL/TLS connection is always established
when new SSL vulnerabilities emerge—as they sometimes do—your CDN provider
This was the case with Heartbleed be protected
Two Are Better Than One
Even with a CDN auto-optimizing the first leg of your SSL connection, it’s still advisable to improve the implementation on the second leg by tweaking the SSL configuration on your origin server.
CDNs for Easy HSTS Activation
HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS) is a security feature that ensures that your domain are a SSL particularly subdomains it can be used
https://www.imperva.com/learn/performance/cdn-and-ssl-tls/
Change the (S)
https://blog.cloudflare.com/microsoft-tls-downgrade-schannel-bug/
Speeding up HTTPS with session resumption
https://calendar.perfplanet.com/2014/speeding-up-https-with-session-resumption/
A cosa –
https://www.evemilano.com/tls-session-resumption/
- CDN uses DNS CNAME record to hide your origin (source) server.
the SOA or primary DNS server
SOA stands for Start Of Authority
CDN can also protect your primary/master DNS server (SOA)
CDN have the ability to “pull” content from their origin server during HTTP requests in order to cache them
GET request, CDN can also proxy POST requests.
check with your CDN provider to block PUT, TRACE, DELETE, CONNECT, which are unsafe HTTP methods.
WAF is not possible to protect all layer 7 attacks
E.g. Application business logic bypass
WAF uses regular expressions to block matching attack patterns
WAF regex needs to be constantly fine tune and improve to block clever attacks
Example: Blind SQL Injection WAF regular expression bypass
CDN WEAKNESS
your origin server's IP address is no longer advertised over DNS, it's still connected to the internet
If your IP address is not kept secret, attackers can bypass the CDN to attack your servers directly
CDN Security Protection Best Practices
Don’t use guessable origin domain name. The attacker can guess the origin system DNS record to bypass the controls. Or using Shodan (http://shodanhq.com)
Disable CDN debugging features. The debugging information can be used by attacks to design a DDoS attack.
Only allow your Origin server to communicate with your CDN servers by white-listing the CDN servers on your firewall.
Only allow your Primary DSN server to communicate with your CDN DNS servers by white-listing the CDN DNS servers on your firewall.
To prevent Direct-to-Origin attacks Subscribe to your ISP Clean-Pipe service or to a Scrubber service provider.
https://www.slideshare.net/AndrewChong7/content-delivery-network-and-web-application-firewall-v12
CDN Debugging Tips: Part 1
When using curl to debug CDN behavior, don't ever use curl -I. Using the I flag results in sending a HEAD request and that is often pointless and unintended. Your users will send GET requests not HEAD requests and the CDN may treat HEAD requests very differently from GET requests. So remember: don't use curl -I, ever
Don't test against just one POP
To send a request to a specific target endpoint (e.g. a CDNetworks server in Amsterdam), use the -H flag to add a Host header with your domain:
https://www.cdnplanet.com/blog/cdn-debugging-tips-part-1/














No comments:
Post a Comment