- Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a network protocol that enables a server to automatically assign an IP address to a computer from a defined range of numbers (i.e., a scope) configured for a given network. When a computer uses a static IP address, it means that the computer is manually configured to use a specific IP address. One problem with static assignment, which can result from user error or inattention to detail, occurs when two computers are configured with the same IP address. This creates a conflict that results in loss of service. Using DHCP to dynamically assign IP addresses minimizes these conflicts. The purpose of DHCP is to ease administration of large networks. With static manual IP configuration you may get network conflict. http://kb.iu.edu/data/adov.html
- How does client know the IP address of DHCP server to send a DHCP Discover Message?
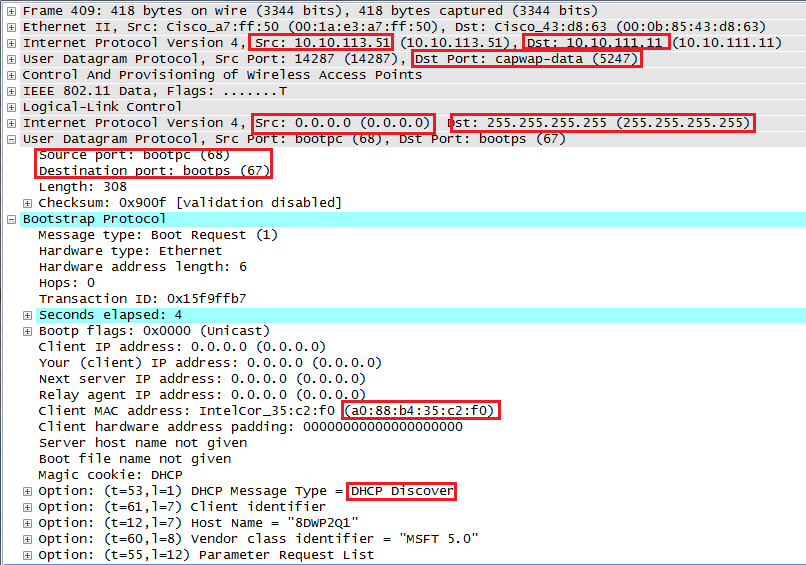
- DHCP Request Message
- How does DHCP (DORA) work?
- APIPA (Automatic Private IP Addressing)
Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA) is a feature in operating systems (such as Windows) that enables computers to automatically self-configure an IP address and subnet mask when their DHCP server isn’t reachable. The IP address range for APIPA is 169.254.0.1-169.254.255.254, with the subnet mask of 255.255.0.0.
https://study-ccna.com/apipa-automatic-private-ip-addressing/








No comments:
Post a Comment