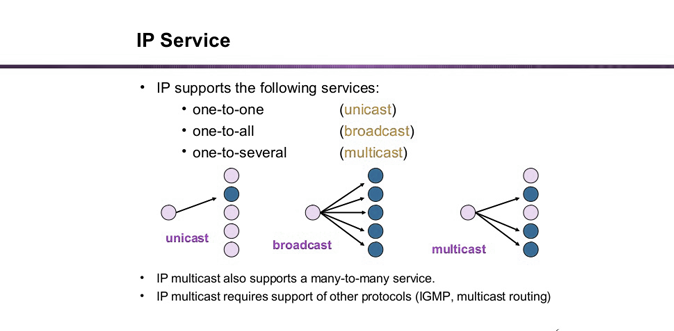
Multicast - A transmission to a group of interface cards on the network.
Broadcast - A transmission to all interface cards on the network.
broadcast- sending information to all the pc's in a network
Multicast-sending infromation to a particular group
unicast-sending information to a particular pc.
unicast,broadcast,multicast
http://www.erg.abdn.ac.uk/~gorry/course/intro-pages/uni-b-mcast.html
- Unicast
Broadcast
Broadcast is the term used to describe communication where a piece of information is sent from one point to all other points. In this case there is just one sender, but the information is sent to all connected receivers
Multicast
Multicast is the term used to describe communication where a piece of information is sent from one or more points to a set of other points. In this case there is may be one or more senders, and the information is distributed to a set of receivers (theer may be no receivers, or any other number of receivers).
http://www.erg.abdn.ac.uk/users/gorry/course/intro-pages/uni-b-mcast.html
- What is Unicast, Broadcast, Multicast & Anycast?
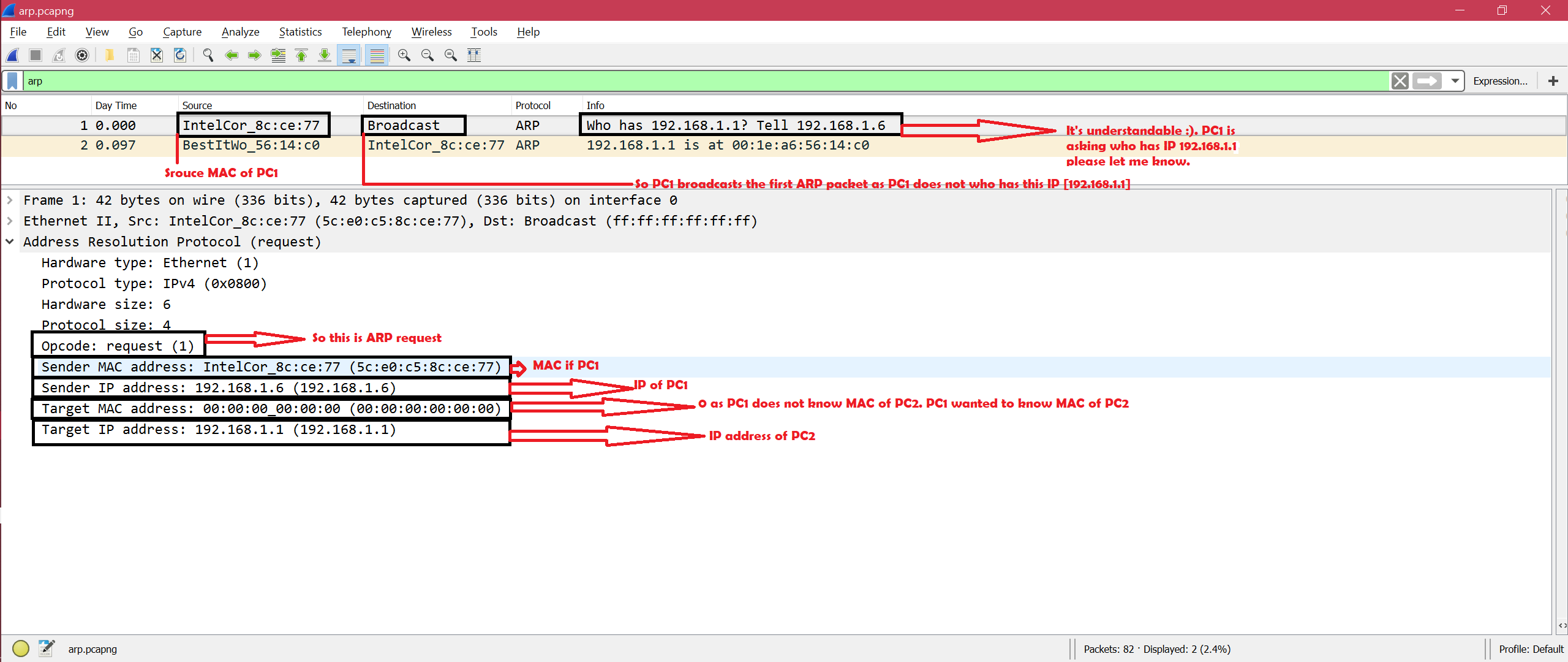
Before a host starts using IP address offered by DHCP server a host should check if this address is not in use by some other host. It is done by ARP probing. An ARP probe is an ARP request that has:
– non-zero Target Protocol Address and Source Hardware Address
– zero Source Protocol Address and Target Hardware Address
Frame 1272: 42 bytes on wire (336 bits), 42 bytes captured (336 bits) on interface 0
Ethernet II, Src: 90:61:ae:fd:41:43, Dst: Broadcast (ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff)
Address Resolution Protocol (request)
Hardware type: Ethernet (1)
Protocol type: IPv4 (0x0800)
Hardware size: 6
Protocol size: 4
Opcode: request (1)
Sender MAC address: 90:61:ae:fd:41:43
Sender IP address: 0.0.0.0
Target MAC address: 00:00:00:00:00:00
Target IP address: 192.168.0.80– non-zero Source Hardware Address and zero Target Hardware Address
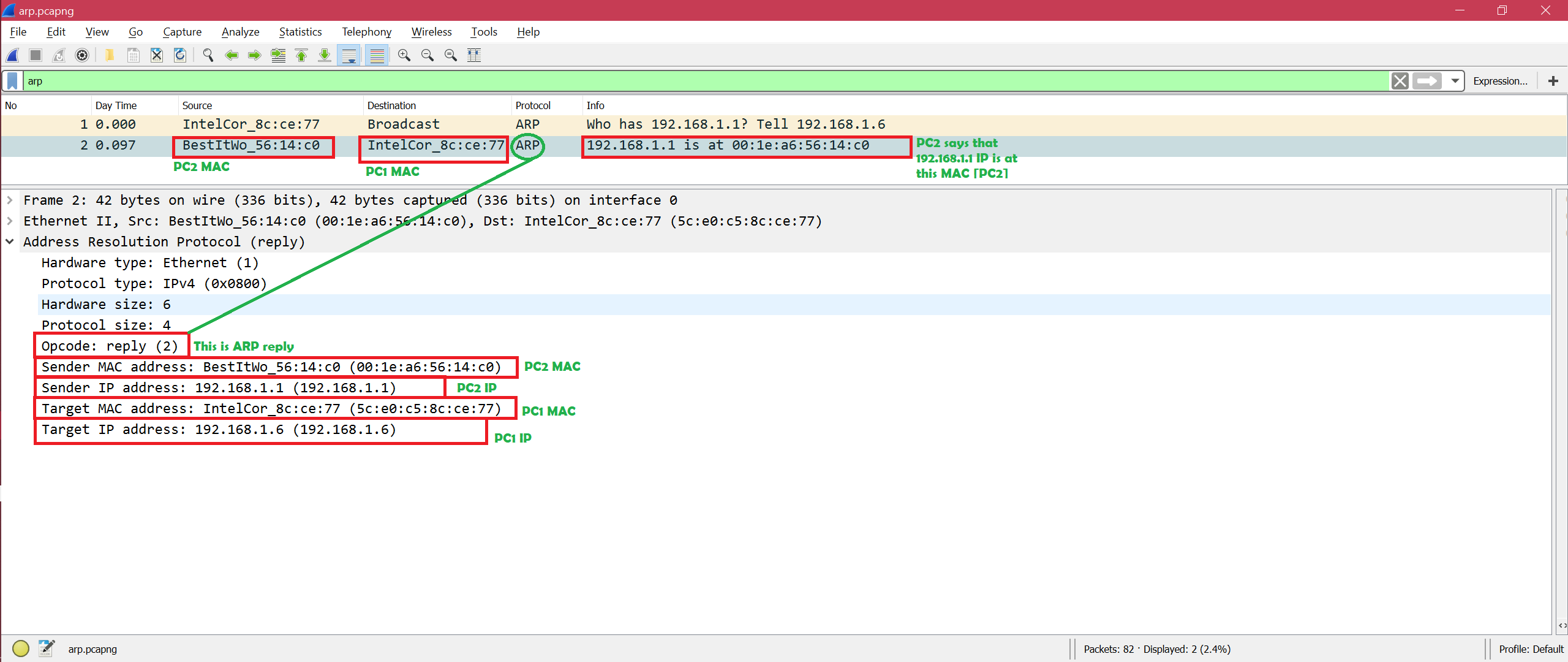
– non-zero (Source Protocol Address and Target Protocol Address) and (Source Protocol Address is equal to Target Protocol Address)
Frame 1911: 42 bytes on wire (336 bits), 42 bytes captured (336 bits) on interface 0
Ethernet II, Src: 90:61:ae:fd:41:43, Dst: Broadcast (ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff)
Address Resolution Protocol (request/gratuitous ARP)
Hardware type: Ethernet (1)
Protocol type: IPv4 (0x0800)
Hardware size: 6
Protocol size: 4
Opcode: request (1)
[Is gratuitous: True]
Sender MAC address: 90:61:ae:fd:41:43
Sender IP address: 192.168.0.80
Target MAC address: 00:00:00:00:00:00
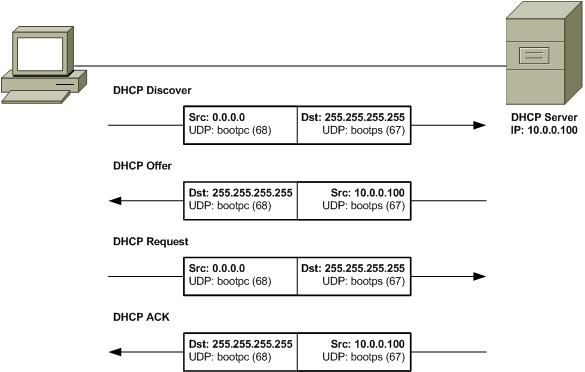
Target IP address: 192.168.0.80- Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is an application layer protocol used to distribute network configuration parameters, such as IP addresses, subnet masks, default gateways, etc. to hosts on a TCP/IP network.
The Server responds with a DHCP Offer (unicast), however if there are many offers from a different DHCP Servers the client accepts the first offer.the offer from the DHCP Server is not an assurance that the IP address will be allocated to the client
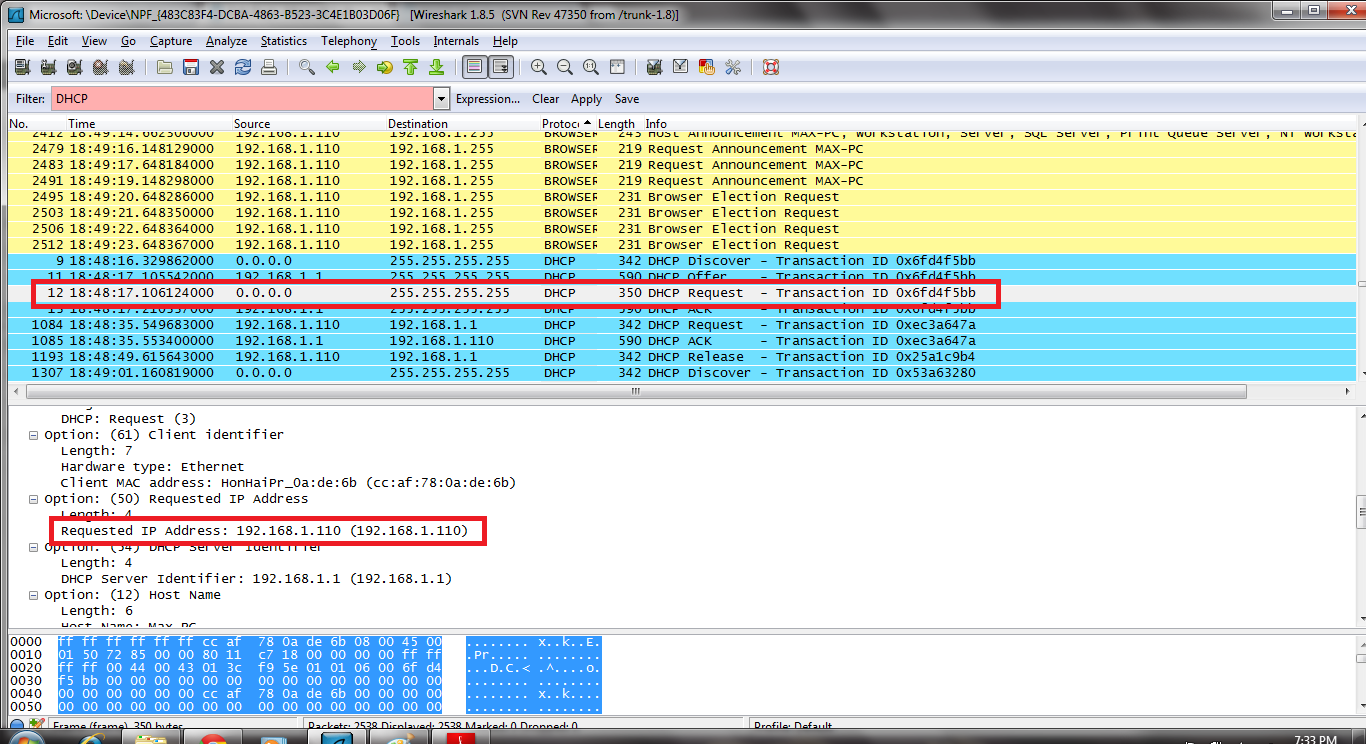
The client sends DHCP Request (Broadcast) that it has accepted the offered IP and it implicitly declines other offers from other servers if any.
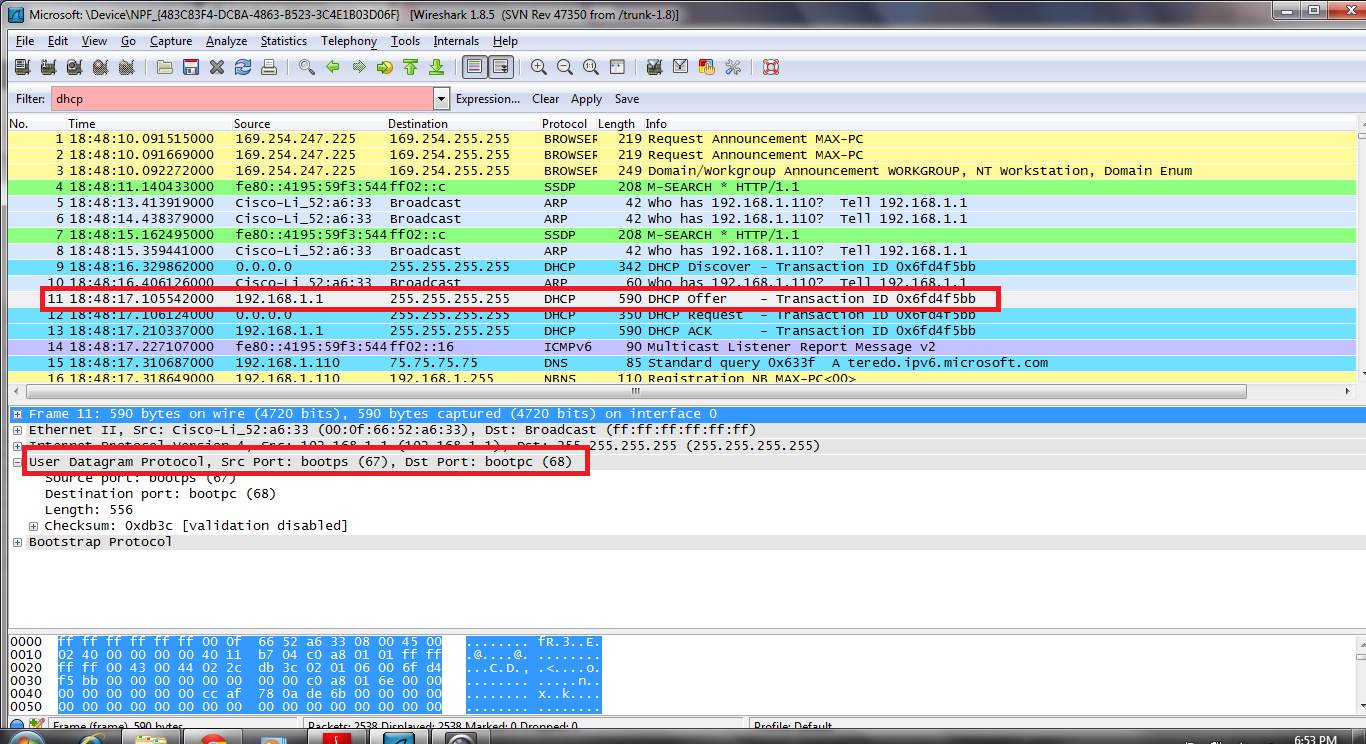
Analysis of DHCP Offer packets in wireshark
The Client IP address is still 0.0.0.0.
This means that IP address has not been assigned to the DHCP Client.
The destination IP address is 255.255.255.255 which means DHCP request is also broadcasted
The IP address that is offered from DHCP Server to DHCP Client is 192.168.43.182
Analysis of DHCP ACK packets in wireshark
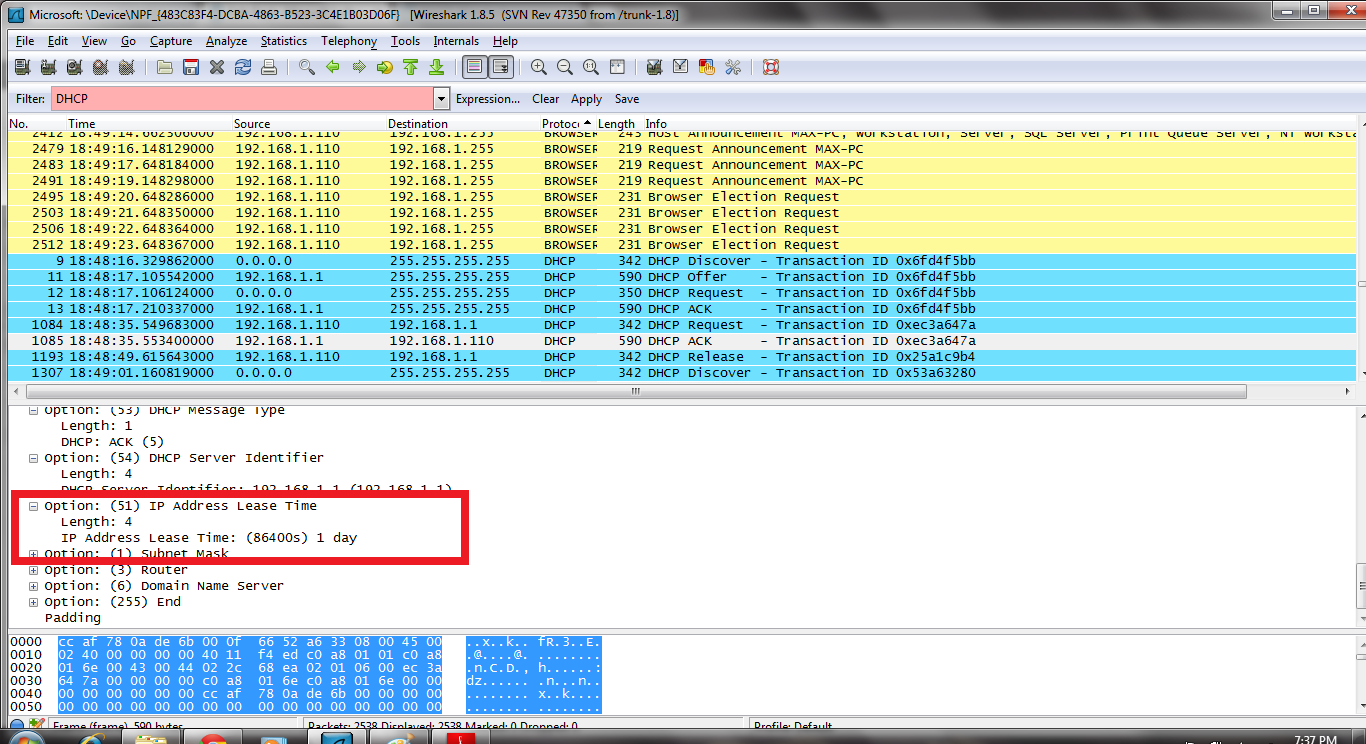
- The subnet mask line tells the client which subnet mask to use.
- The router line indicates where the client should send messages by default.
- The purpose of the release message is to release the IP address back to the server.
- There is no verification that the release message has been received by the server.
- If the message is lost, the client releases the IP address, but the server will not reassign that address until the clients lease on the address expires.
- Discover: 0.0.0.0/255.255.255.255
- Offer: 192.168.1.1/255.255.255.255
- Request: 0.0.0.0/255.255.255.255
- ACK:192.168.1.1/255.255.255.255
- 192.168.1.1
1. Begin by opening the Windows Command Prompt application. As shown in Figure 1, enter “ipconfig /release”.
2. Start up the Wireshark packet sniffer, as described in the introductory Wireshark lab and begin Wireshark packet capture.
3. Now go back to the Windows Command Prompt and enter “ipconfig /renew”. This instructs your host to obtain a network configuration, including a new IP address. In Figure 1, the host obtains the IP address 192.168.1.108
4. Wait until the “ipconfig /renew” has terminated. Then enter the same command “ipconfig /renew” again.
5. When the second “ipconfig /renew” terminates, enter the command “ipconfig/release” to release the previously-allocated IP address to your computer.
6. Finally, enter “ipconfig /renew” to again be allocated an IP address for your computer.
7. Stop Wireshark packet capture.











No comments:
Post a Comment