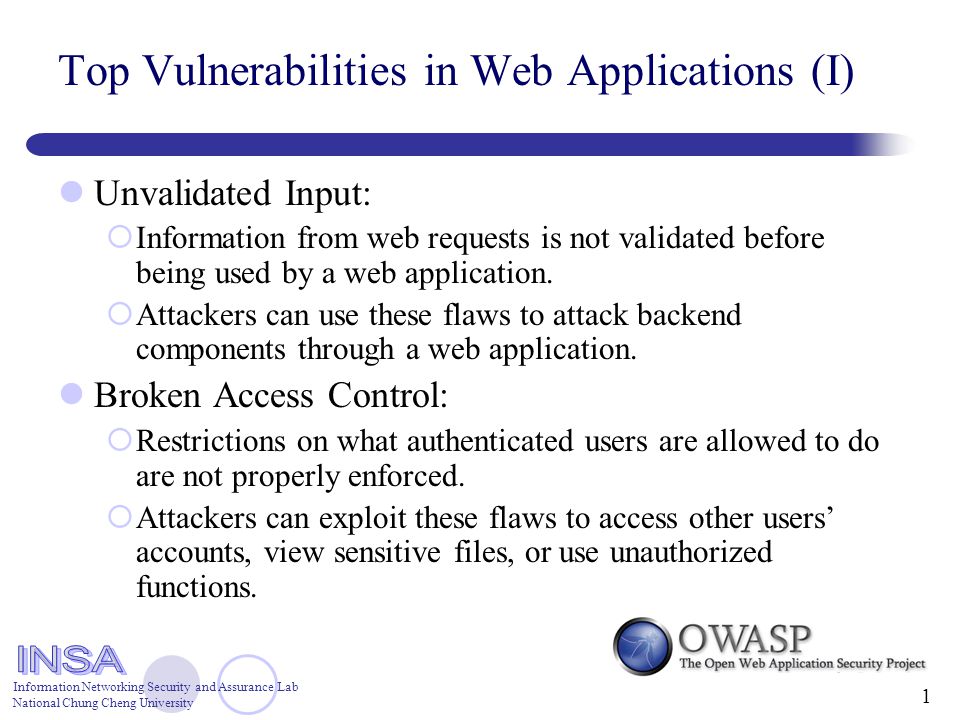
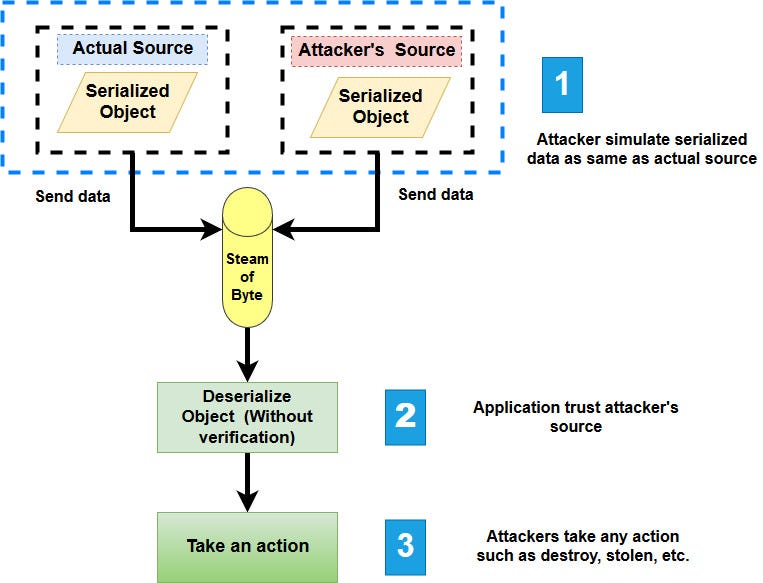
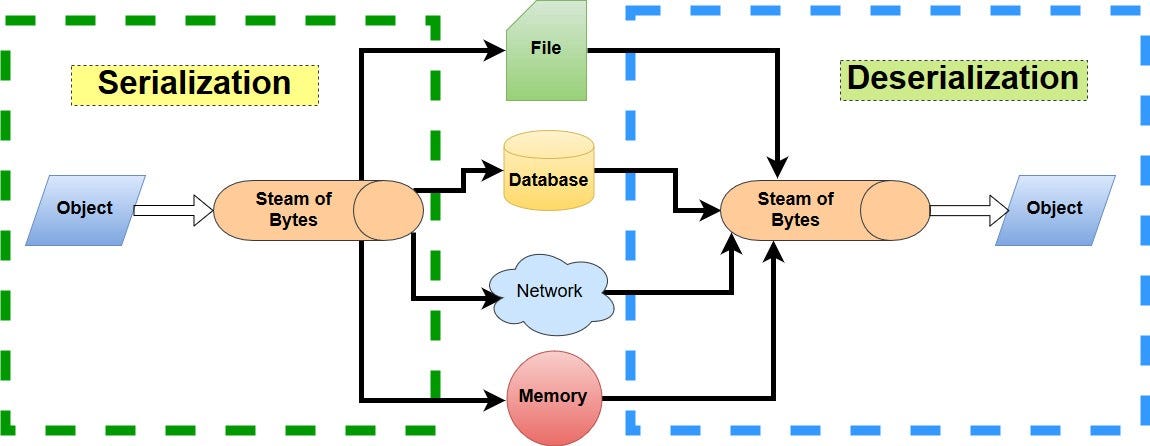
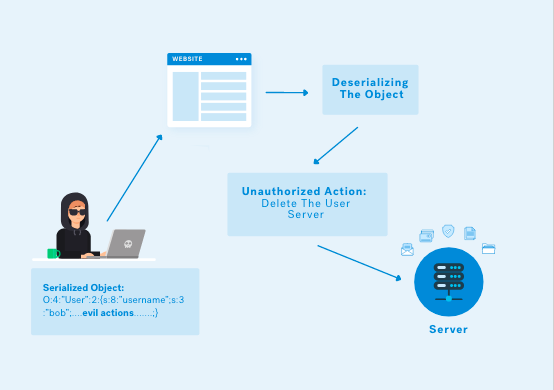
- The EMC® CLARiiON® CX4 series delivers industry-leading innovation in midrange storage with the fourth-generation CLARiiON CX™
storage platform. The unique combination of
flexible,scalable hardware design and Advanced Storage Efficiency products enables the CX4 series
systems, powered by Intel
Xeon processors, to meet the growing, diverse needs of today’s midsize and large enterprises.
http://www.emc.com/collateral/hardware/data-sheet/h5527-emc-clariion-cx4-ds.pdf
Provides unified block, file, and object support
Delivers high performance and low latency with
MCx multicore optimization
Supports 1 PB max raw capacity
Reduces capacity needs with block-based and file-based deduplication and compression
Offers industry-leading integration with
VMware and Microsoft Hyper-V virtualization
Pairs with FAST Suite to optimize performance and cost
Simplifies administration with EMC Unisphere Management Suite
https://store.emc.com/us/Solve-For/STORAGE-PRODUCTS/VNX5400/p/VNX-VNX5400-storage-platform
Object-based cloud storage platform to store, archive and access unstructured content at scale.
Atmos provides the essential building blocks for enterprises and service providers to transform to private, hybrid, and public cloud storage.
http://turkey.emc.com/storage/atmos/atmos.htm
Seamlessly integrating best-in-class
compute, network, and storage technologies from industry leaders Cisco, EMC, and
VMware
http://www.vce.com/products/converged/vblock/overview
- EMC Unisphere is the next generation unified storage management
platform that provides intuitive user interfaces for the newest range of
unified platforms including the EMC VNX and EMC VNXe series
EMC Unisphere presents a new approach to unified storage
management through a simple, flexible, and integrated user experience.
Information
is consolidated and visible through a single lens and
managing storage
is simplified by providing an intuitive, context-based
approach. Users can customize their view and easily reallocate data.
Unisphere also provides users with an extensive network of support and
collaboration with other users.
http://turkey.emc.com/corporate/glossary/unisphere.htm
Cisco UCS Integrated Infrastructure Solutions speed up IT
operations today and create the modern technology foundation you need
for initiatives like private cloud, big data, and desktop
virtualization. Cisco UCS Director provides centralized automation of
your physical and virtual resources, helping you take full advantage of
our open ecosystem approach.
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/servers-unified-computing/index.html
- EMC NetWorker backup and recovery software centralizes, automates, and accelerates data backup and recovery across your IT environment. NetWorker delivers record-breaking performance and a wide range of data protection options to safeguard your critical business data.
http://www.emc.com/data-protection/networker.htm
the ESRS Virtual Edition
EMC Secure Remote Services
Some additional benefits you can expect with ESRS v3:
Simplified installation and implementation process
No more dedicated servers, physical hardware, and OS licensing fees
Real-time audit of remote support activities through an intuitive user interface
Improved reliability with built-in optional failover to alternate connectivity methods such as email-home and FTPS
https://community.emc.com/servlet/JiveServlet/downloadImage/38-10383-93764/670-313/ESRS+v3+architecture.png
- ESRS stands for EMC Secure Remote Support. The main benefit of ESRS is to enable EMC to deliver proactive customer service by identyfying and addressing potential problems before there is an impact to the customer’s business.
http://www.storagefreak.net/2014/07/emc-esrs-basic-overview
- EMC Storage Performance Monitoring
SolarWinds® Storage Resource Monitor enables comprehensive EMC® SAN and NAS performance and capacity monitoring to help avoid downtime. With an easy-to-use Web-based UI, go deeper to retrieve performance and capacity information for your entire EMC storage ecosystem
http://www.solarwinds.com/solutions/emc-storage-performance.aspx
SINGLE TOOL FOR MANAGING VMWARE AND EMC ENVIRONMENTS
http://www.emc.com/collateral/hardware/data-sheet/h11853-storage-analytics-vnx-ds.pdf
- RecoverPoint 4.0 introduces the virtual RecoverPoint Appliance (vRPA) option for EMC VNX unified storage.
Now a growing number of mid-sized organizations can
benefit from RecoverPoint’s DVR-like rollback capability and realize any point-in-time recovery for their most mission-critical applications. With EMC RecoverPoint, one solution protects any host, any application, on any array, physical or virtual.
packaged to run on a virtual machine.
EMC
RecoverPoint Continuous Data Protection (CDP) technology provides a selectable Recovery Point
Objective (RPO) so you can roll-back to that moment in time just before your data became corrupted or lost.
RecoverPoint 4.0 is the industry’s first replication product to recover a virtual machine to ANY point-in-time in a
VMware SRM Test or
Failover vs. having to settle for the last point in time. Perfect for rapidly recovering from major issues like viruses or data corruption.
http://pulseblog.emc.com/2013/04/30/recoverpoint-4-0-changes-the-replication-economics-for-vnx/
- EMC RecoverPoint replication provides the continuous data protection you need to recover any application, on any storage array, in any location, to any point in time.
Optimize your RTO and RPO targets by ensuring instant access to data for disaster recovery, operational recovery, and testing. Use
RecoverPoint to extend
VMware Site Recovery Manager (SRM) beyond snapshots.
Choose the RecoverPoint Appliance (RPA) for highest performance, or install RecoverPoint Virtual Edition for VNX with the virtual RPA (
vRPA) for up to 33% lower cost.
https://store.emc.com/us/Solve-For/STORAGE-PRODUCTS/EMC-RecoverPoint/p/EMC-RecoverPoint
Brocade DCX 8510 Backbones are the industry’s most powerful Fibre Channel switching infrastructure, providing the most reliable, scalable, high-performance foundation for private cloud storage and highly virtualized environments.
They are designed to increase business agility while providing non-stop access to information and reducing infrastructure and administrative costs.
http://www.brocade.com/products/all/san-backbones/product-details/dcx8510-backbone/index.page
http://www-03.ibm.com/systems/networking/switches/san/
http://www.emc.com/products/family/celerra-family.htm
http://www.netapp.com/us/products/protocols/san/san.html
http://h18006.www1.hp.com/products/storage/software/sanvr/index.html
http://h18006.www1.hp.com/storage/nas/index.html
- The Unified Computing System (UCS) fabric interconnect is a networking switch or head unit where the UCS chassis, essentially a rack where server components are attached, connects to.
https://www.techopedia.com/definition/30473/ucs-fabric-interconnect
- Cisco HyperFlex Distributed Storage
Each node includes a Cisco
HyperFlex HX Data Platform controller that implements the distributed file system using internal flash-based SSD drives and high-capacity HDDs to store data. The controllers communicate with each other over 10 Gigabit Ethernet to present a single pool of storage that spans the nodes in the cluster
https://gblogs.cisco.com/ch-tech/hyperflex-architecture-and-how-it-works/
- HP Virtual Connect FlexFabric
HP Virtual Connect FlexFabric 10Gb/24-port Modules are the simplest, most converged and flexible way to connect virtualized server blades to any data or storage network. VC FlexFabric modules eliminate up to 95% of network sprawl at the server edge with one device that converges traffic inside enclosures and directly connects to LANs and SANs.
http://www8.hp.com/us/en/products/virtual-connects/product-detail.html?oid=4144088
- HP EML E-Series Tape Libraries
The HP Enterprise Modular Library (EML) E-Series Tape Libraries provide reliability, scalability and manageability with robust data
protection and investment protection in heterogeneous Storage Area Network (SAN) environments. The EML delivers superior data
availability with protection against SAN event disruptions using the built in HP Extended Tape Library Architecture (ETLA)
http://www8.hp.com/h20195/v2/GetPDF.aspx/c04140830.pdf
- HP Continuous Access EVA Software
Protects valuable data by replicating from one HP Enterprise Virtual Array (EVA) to another - providing advanced disaster recovery with ease of management
http://h18006.www1.hp.com/products/storage/software/conaccesseva/index.html
- HP Storage Mirroring Software
Proactive replication reduces risks and keeps a business running when the unforeseen occurs.
http://h18006.www1.hp.com/products/storage/software/sm/index.html
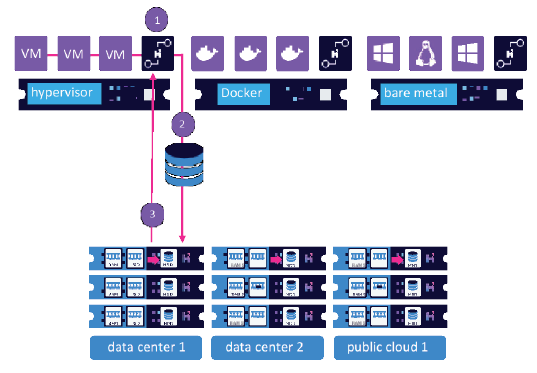
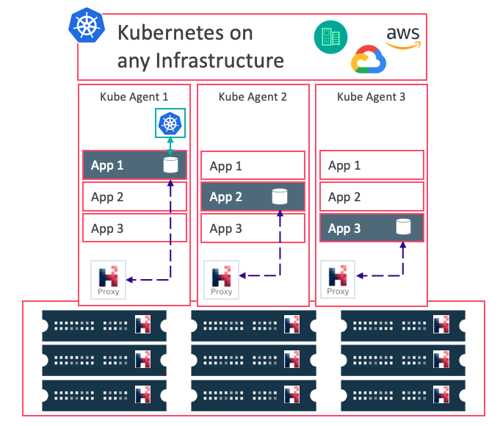
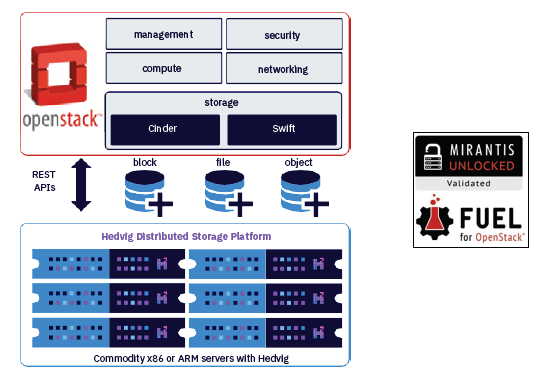
- HyperScale X is the latest generation of Commvault’s fully integrated scale-out data management solution, and is the first product in the portfolio to integrate technology from the recent Hedvig acquisition.
Commvault Hyperscale X is an intuitive and easy to deploy scale-out appliance that is fully integrated with Commvault’s intelligent data management platform. Integrated with the power of Commvault Hedvig, Hyperscale X provides unmatched scalability, security and resiliency to accelerate an organization’s digital transformation journey as they move to hybrid cloud, container and virtualized environments. Its flexible architecture allows customers to get up and running quickly and grow as their needs demand.
https://www.commvault.com/news/commvault-launches-hyperscale-x-marking-first-portfolio-integration-of-hedvig-technology