- How to Configure the DHCP Relay Agent
The DHCP relay service allows you to pass DHCP broadcast messages to network segments that a client computer is not directly attached to. DHCP relaying can be used to share a single DHCP server across logical network segments that are separated by a firewall. The DHCP relay service does not handle IP addresses. It sends unicast messages instead of broadcast messages.
A client in need of a DHCP-assigned IP address sends its request as a broadcast message to the network attached to the corresponding interface. The DHCP relay service on the firewall receives the request on an interface attached to the same network, e.g., eth2, 192.168.0.0/24. The DHCP relay service sends a unicast request to all configured DHCP servers in the LAN and receives a DHCP IP address offer from a DHCP server (e.g., 10.0.0.254) that has an IP address range configured for the network segment of the requesting client (e.g., 192.168.0.0/24). This offer is forwarded to the requesting client. If the client accepts the offer, the DHCP address is acknowledged by the client and immediately assigned to its attached interface.
https://campus.barracuda.com/product/cloudgenfirewall/doc/78153918/how-to-configure-the-dhcp-relay-agent/
- How to configure DHCP Relay on Cisco ASA Firewall
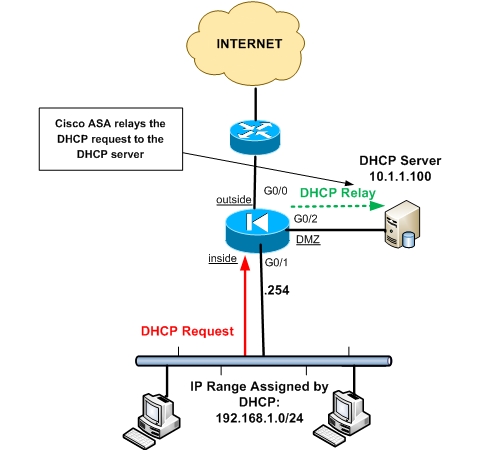
Usually the DHCP server is located in the same layer 3 subnet with its clients. There are situations however where we have only one DHCP server but several layer 3 networks exist (on different security zones on a Cisco ASA) and dynamic IP allocation is required for those networks as well
The three network zones are inside, outside and DMZ. The DHCP clients are connected to the inside network and the DHCP server on the DMZ network. The DHCP requests from the clients on the inside network will be relayed to the server on the DMZ network. The server will assign IP addresses in the range 192.168.1.0/24 to the clients.
Use Cases
Suppose you have an internal network with many Layer3 subnets. There is internal network segmentation using Layer2 VLANs and each Layer3 subnet might be connected to a different security zone on the ASA firewall.
Let’s say we have a Windows servers environment with Active Directory and a Windows DHCP server located in one network subnet. This DHCP server must allocate IP addresses dynamically to all hosts in the network, irrespective of which network segment each host is connected.
https://www.networkstraining.com/how-to-configure-dhcp-relay-on-cisco-asa-firewall/
- How to Configure a DHCP Relay on Palo Alto Networks Firewall
Verification
Test on a client. For example, a Windows Client:
ipconfig /release
ipconfig /renew
ipconfig /all
The DHCP Server must route the DHCP traffic to the Palo Alto Networks firewall for this configuration to work. Issues will arise if the DHCP server has another default gateway instead of the Palo Alto Networks firewall (or is not directly connected and routing the return traffic somewhere else). The DHCP traffic is then considered asymmetric. If the DHCP server traffic is asymmetric, the session is not setup properly on the firewall and the complete DHCP communication is not complete.
https://knowledgebase.paloaltonetworks.com/KCSArticleDetail?id=kA10g000000ClFXCA0
- Cascading DHCP Relay Agents with Interfaces to be Configured
When you configure the relay agents, the interfaces listening to broadcast requests from the clients (eth1 and eth4) must be specified as relay interfaces. The server-side interface of relay agent 2 (eth5), which is connected to the DHCP server, must NOT be specified.
https://campus.barracuda.com/product/cloudgenfirewall/doc/73007431/how-to-configure-the-dhcp-relay-agent/
- DHCP Relay Agent Overview
A DHCP relay agent is any host that forwards DHCP packets between clients and servers. Relay agents are used to forward requests and replies between clients and servers when they are not on the same physical subnet. Relay agent forwarding is distinct from the normal forwarding of an IP device, where IP datagrams are switched between networks somewhat transparently. By contrast, relay agents receive DHCP messages and then generate a new DHCP message to send out on another interface. The relay agent sets the gateway IP address (giaddr field of the DHCP packet) and, if configured, adds the relay agent information option (option82) in the packet and forwards it to the DHCP server. The reply from the server is forwarded back to the client after removing option 82.
The DHCP relay agent supports the use of unnumbered interfaces. An unnumbered interface can “borrow” the IP address of another interface already configured on the device, which conserves network and address space. For DHCP clients connected though the unnumbered interfaces, the DHCP relay agent automatically adds a static host route once the DHCP client obtains an address, specifying the unnumbered interface as the outbound interface. The route is automatically removed once the lease time expires or when the client releases the addres
https://content.cisco.com/chapter.sjs?uri=/searchable/chapter/content/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/ipaddr_dhcp/configuration/15-sy/dhcp-15-sy-book/configuring_cisco_ios_dhcp_relay_agent.html.xml
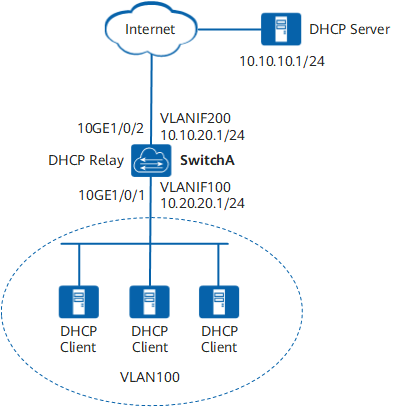
an enterprise uses a DHCP server to assign IP addresses to servers in the data center. The server at 10.20.20.0/24 is used as an example to describe how to configure a DHCP relay agent.
The enterprise client is on the network segment 10.20.20.0/24, and the DHCP server is on the network segment 10.10.10.0/24. The DHCP clients can obtain IP addresses from the DHCP server through SwitchA enabled with DHCP relay.
The uplink interface of SwitchA is 10GE1/0/2, the address of VLANIF 200 is 10.10.20.1/24, and the interface address of SwitchA connected to the peer device is 10.10.20.2/24.
The public address of the DHCP server is 10.10.10.1/24 and the interface address of the DHCP server connected to the peer device is 10.10.10.2/24
https://support.huawei.com/enterprise/it/doc/EDOC1000039339/d7f419bb/example-for-configuring-a-dhcp-relay-agent
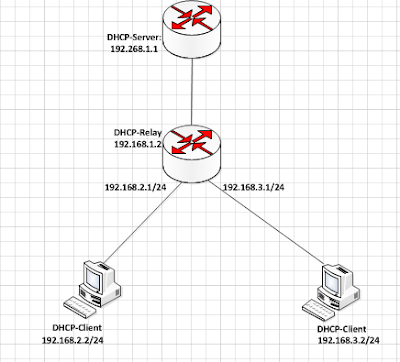
The DHCP relay feature is used to provision a Mikrotitik router to act as a DHCP server on behalf of the real DHCP server.
the dhcp server is on the same network with the dhcp relay while the dhcp clients are not on the same network as the dhcp server. The dhcp relay, in turn, is on the same network with the hosts. When a dhcp request is sent from network hosts, the dhcp relay receives it and forwards the request to the dhcp server.
The question on most people’s mind at this point is, why do I need a dhcp relay? Why can’t I just configure a dhcp server instead. Well, in a nutshell, a dhcp relay agent is used to forward dhcp requests and replies between a dhcp server and clients who are not on the same subnets.
https://www.timigate.com/2018/02/how-to-provision-mikrotik-router-as.html