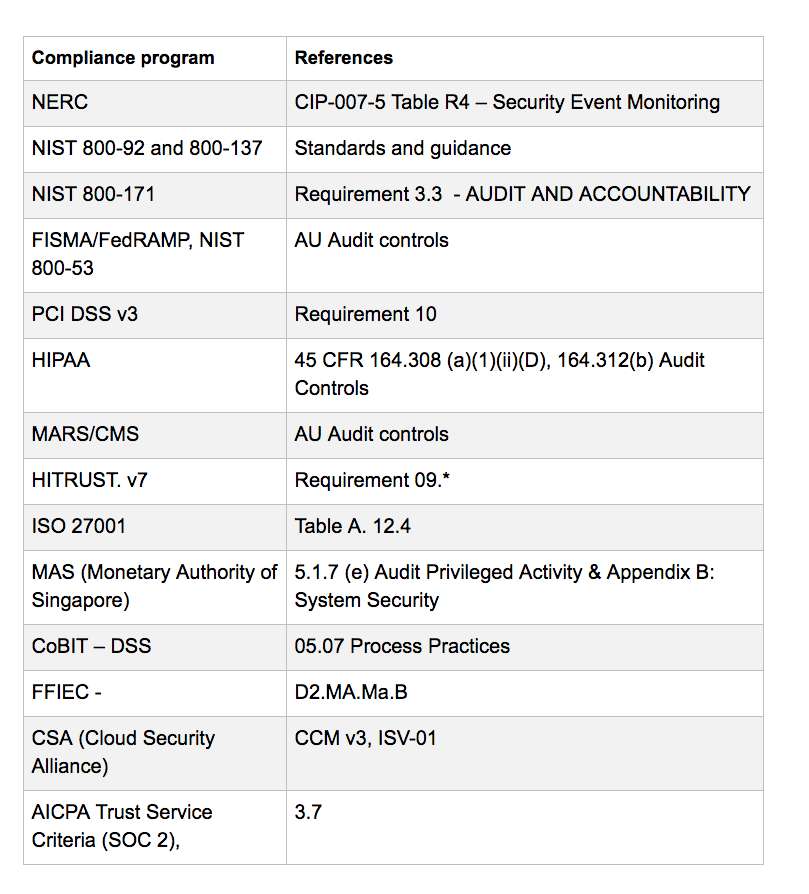
- What is an Audit Trail in IT Context?
Audit trails maintain a record of system activity both by system and application processes and by user activity of systems and applications
the audit trail includes all or some of the following
Application-specific audit trail
Application logs
Database logs
Operating system logs
Access logs
Network logs
Once the audit trails
Availability
A secure audit trail allows organizations to:
Identify that something wrong has happened
Prove what happened and who did it
Reconstruct the original data
Be compliant.
https://logsentinel.com/what-is-an-audit-trail-in-it-context/
- Security Audit Logging Guideline
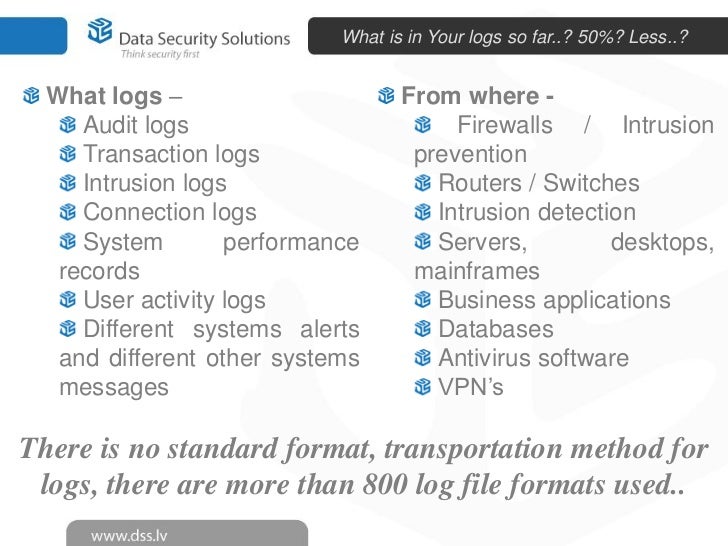
Regular log collection is critical to understanding
Logs are also useful for establishing baselines, identifying operational trends and supporting the organization’s internal investigations, including audit and forensic analysis
Log events in an audit logging program should at
Operating System
start up and down of a service
network connection changes or failures
changes to, or attempts to
OS Audit Records
log on attempts (successful or unsuccessful)
the function
account changes (e.g., account creation and deletion, account privilege assignment)
successful/failed use of privileged accounts
Application Account Information
successful and failed application authentication attempts
application account changes (e.g., account creation and deletion, account privilege assignment)
use of application privileges
Application operations
application startup and shutdown
application failures
major application configuration changes
application transactions, for example,
e-mail servers recording the sender, recipients, subject name, and attachment names for each e-mail
Web servers recording each URL requested and the
The details logged for each event may
timestamp
event, status, and/or error codes
service/command/application name
user or system account associated with an event
Device used (e.g. source and
https://security.berkeley.edu/security-audit-logging-guideline
- a long line or a series of marks that have
been left
https://www.ldoceonline.com/dictionary/trail
- A log is a recording of what happens on a system
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Log_file
- An audit trail is a recording of all user actions
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Audit_trail
- The logs show
, in detail as well as
collecting, centrally aggregating, storing and
The importance of these logs isn’t in the logging itself. Instead, it’s the analysis of these logs
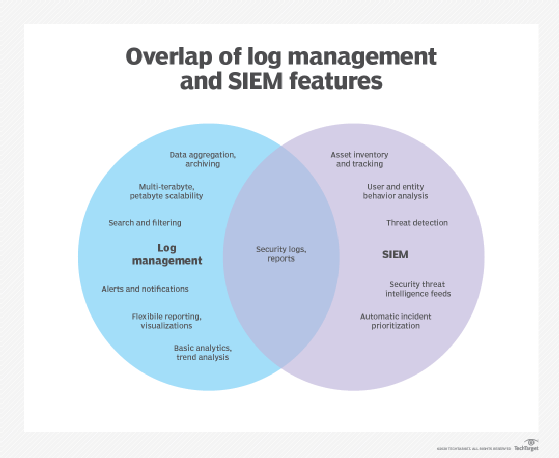
SIEM, though, is a significant step beyond log management.
Log management (LM), as previously described, which collects and stores log files from operating systems and
Security event management (SEM), which focuses on real-time monitoring, correlating events, providing overarching console views, and customizing notifications.
Security information management (SIM), which provides long-term storage, analysis, manipulation, and reporting on logs and security records.
Security event correlation (SEC), which tracks and alerts designated administrators when a peculiar sequence of events occurs, such as three failed login attempts under the same
Benefits of SIEM
Like log management, the goal of SIEM is security
https://www.bmc.com/blogs/siem-vs-log-management-whats-the-difference/
- What is File Integrity Monitoring (FIM)?
FIM solutions monitor file changes on servers, databases, network devices, directory servers, applications, cloud environments, virtual images and to alert you to unauthorized changes
FIM helps you meet many regulatory compliance standards like PCI-DSS, NERC CIP, FISMA, SOX, NIST and HIPAA,
File Change Detection
File integrity monitoring, in its simplest sense, is about keeping track of change from an established baseline and alerting you to any unexpected change that may represent a security risk or a compromise in regulatory compliance
Baseline Comparison
Automated Remediation
Once your FIM solution flags a suspicious change from your established security baseline, it should provide immediate steps for remediation. Automated FIM solutions help you return to your baseline quickly. Advanced FIM products can also integrate with other security solutions like log management, vulnerability management and security configuration management (SCM),
https://www.tripwire.com/solutions/file-integrity-and-change-monitoring/what-is-fim/
https://www.ionx.co.uk/products/verisys
- Auditing is used to answer the question "Who did what?" and possibly why. Logging is more focussed on what's happening.
- syslog is a general logging daemon available for any application or the system to use for any reason. The audit daemon's job is to track specific activities or events to determine who did what and when.
- Auditing often has legal requirements.
- Auditing
Business level events
Information for users and clients
Who did what, when
Often required legally or by the client contract
Usually kept indefinitely or at least for legally specified period
Logging
Program level events
Information for developers and support
What happend, incl debug informations
Required for maintenance or debugging purposes
Often deleted after a short time