- Personal data, also known as personal information,
or sensitive personal information (SPI)
is any information relating to an identifiable person.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Personal_data
- Personally Identifiable Information (PII)
Personally Identifiable Information (PII) is a category of sensitive information that
Protected Health Information (HIPAA)
Protected Health Information (PHI)
https://safecomputing.umich.edu/dataguide/?
- What is CUI, CDI and CTI Data?
Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) and Covered Defense Information (CDI) are relatively new markings, but similar markings have a long history within the government. CDI is an umbrella term that encompasses all CUI and Controlled Technical Information (CTI).
How do I protect CUI/CDI/CTI data?
The government provided lane markers as part of the DFARS 7012 rule that stipulates exactly what type of controls must be in place to protect CUI/CDI content in your information system. You have three options.
An on-premises data center
A Cloud Service Provider (CSP) like Azure, Office 365, or Amazon Web Services (AWS), or
A Hybrid Solution that uses both on-premises systems and CSP solutions to meet NIST 800-171.
With any of these three solutions, you
https://info.summit7systems.com/blog/cui
- Data anonymization
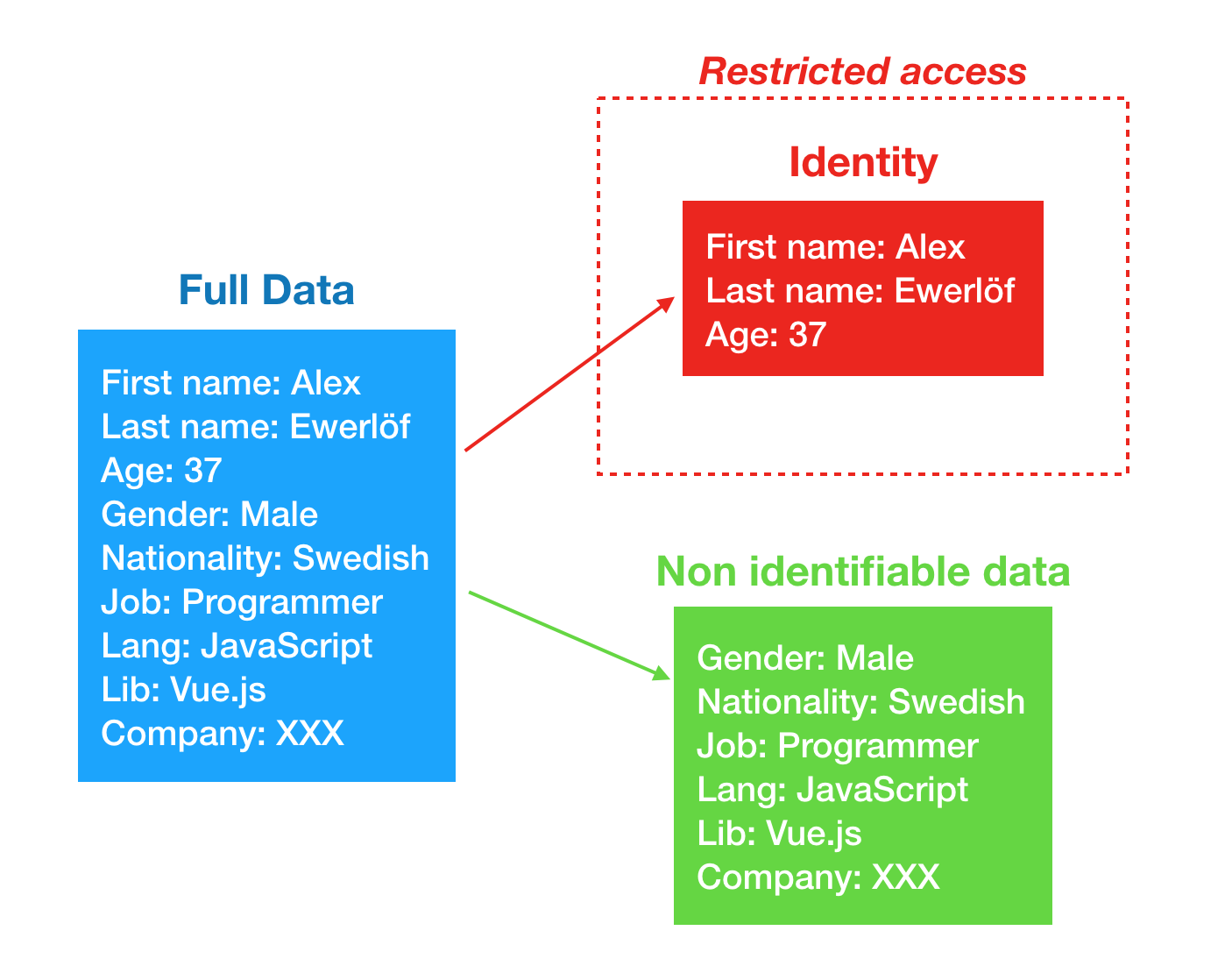
Data anonymization is a type of information sanitization whose intent is privacy protection. It is the process of removing personally identifiable information from data sets, so that the people whom the data describe remain anonymous. The European Union's new General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) demands that stored data on people in the EU undergo either an anonymization or a pseudonymization process.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Data_anonymization
- Pseudonymization
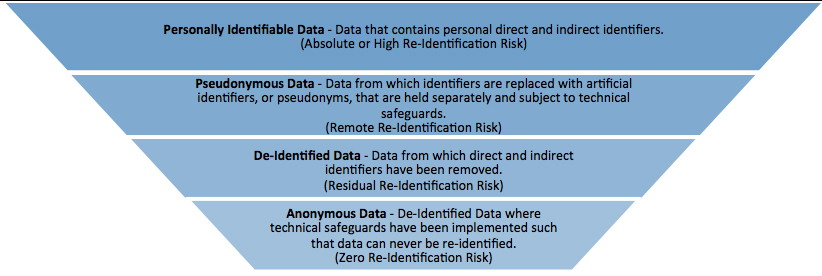
Pseudonymization is a data management and de-identification procedure by which personally identifiable information fields within a data record are replaced by one or more artificial identifiers, or pseudonyms. A single pseudonym for each replaced field or collection of replaced fields makes the data record less identifiable while remaining suitable for data analysis and data processing
Pseudonymization (or pseudonymisation) can be one way to comply with the European Union's new General Data Protection Regulation demands for secure data storage of personal information
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pseudonymization
- Pseudonymization vs. Anonymization and How They Help With GDPR
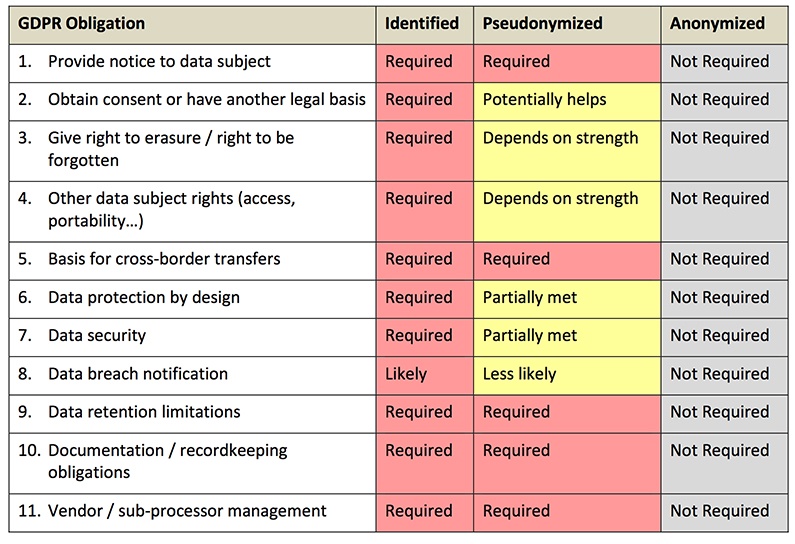
Pseudonymization and Anonymization are different in one key aspect. Anonymization irreversibly destroys any way of identifying the data subject. Pseudonymization substitutes the identity of the data subject in such a way that additional information is required to re-identify the data subject
Tokenization provides a consistent token for each unique name and requires access to additional information (our static lookup tables/code books) to re-identify the data
with the pseudonymized data, we may not know the identity of the data subject, but we can correlate entries with specific subjects
If we have access to re-identify the data via the token lookup tables, then we can get back to the real identity. With the anonymized data, however, we only know that there are 7 records and there is no method to re-identify the data.
With Anonymization, we must also be concerned about “indirect re-identification”.We might not be able to identify the name, but we might be able to identify that specific books were written by the same person, because of their unique writing style.If that author has also written something under their own name, we might be able to completely identify the individual, by comparing the anonymous writing style with known author styles.
To properly anonymize this data, we might have to use additional methods to ‘hide’ individual behavior.
https://www.protegrity.com/blog/pseudonymization-vs-anonymization-help-gdpr






No comments:
Post a Comment