- 1. Explain risk, vulnerability and threat?
Vulnerability (weakness) is a gap in the protection efforts of a system, a threat is an attacker who exploits that weakness. Risk is the measure of potential loss when that the vulnerability is exploited by the threat
2. What is the difference between Asymmetric and Symmetric encryption and which one is better?
Symmetric encryption uses the same key for both encryption and decryption, while Asymmetric encryption uses different keys for encryption and decryption.
Symmetric is usually much faster but the key needs to be transferred over an unencrypted channel. Asymmetric on the other hand is more secure but slow.
Hence, a hybrid approach should be preferred. Setting up a channel using asymmetric encryption and then sending the data using a symmetric process.
4. What is XSS, how will you mitigate it?
Cross site scripting is a JavaScript vulnerability in web applications.
when a user enters a script in the client-side input fields and that input gets processed without getting validated.
This leads to untrusted data getting saved and executed on the client-side. Countermeasures of XSS are input validation, implementing a CSP (Content security policy)
5. What is the difference between encryption and hashing?
Encryption is reversible whereas hashing is irreversible. Hashing can be cracked using rainbow tables and collision attacks but is not reversible.
Encryption ensures confidentiality whereas hashing ensures Integrity.
7. What is CSRF?
Cross-Site Request Forgery is a web application vulnerability in which the server does not check whether the request came from a trusted client or not. The request is just processed directly
13. CIA triangle?
Confidentiality: Keeping the information secret.
Integrity: Keeping the information unaltered.
Availability: Information is available to the authorised parties at all times.
14. HIDS vs NIDS and which one is better and why?
HIDS is a host intrusion detection system and NIDS is a network intrusion detection system. Both the systems work on similar lines. It’s just that the placement is different. HIDS is placed on each host whereas NIDS is placed in the network. For an enterprise, NIDS is preferred as HIDS is difficult to manage, plus it consumes the processing power of the host as well.
20. Various response codes from a web application?
1xx – Informational responses
2xx – Success
3xx – Redirection
4xx – Client-side error
5xx – Server side error
30. What is a false positive and false negative in case of IDS?
When the device generated an alert for an intrusion that has actually not happened: this is a false positive and if the device has not generated any alert and the intrusion has actually happened, this is the case of a false negative.
https://www.siemxpert.com/blog/soc-analyst-interview-question/
- Question 4: What is the three-way handshake?
Three-way handshake mechanism: In this mechanism, the client sends an SYN TCP packet to the server asking for a connection (synchronizing) request and a sequence number. The server responds with the SYN/ACK packet, acknowledging the connection request and assigning a sequence number. The client again sends an ACK packet to accept the response of the server.
Question 6: What is data leakage? Explain in your own words.
Answer: Data leakage refers to the exposure or transmission of an organization’s sensitive data to the external recipient. The data may be transmitted or exposed via the internet or by physical means.
Question 7: List the steps to develop the Data Loss Prevention (DLP) strategy?
Answer: The steps to develop and implement a DLP strategy are as follows:
Step1: prioritizing the critical data assets
Step2: categorizing the data based on its source
Step3: analyzing which data is more prone to the risks
Step4: monitor the transmission of the data
Step5: developing control measures to mitigate the data leakage risk
Question 8: What is the difference between TCP and UDP?
TCP(Transfer Layer Protocol)
TCP is reliable as it guarantees the delivery of data packets to the destination.
TCP is heavyweight.
TCP is slower as compared to UDP
Example: HTTP, SSH, HTTPS, SMTP
UDP(User Datagram Protocol)
UDP is not reliable as it does not guarantees the delivery of data packets to the destination
UDP is lightweight.
UDP IS faster than TCP
Example: TFTP, VoIP, online multiplayer gamess
Question 9: What is the difference between firewall deny and drop?
Answer: DENY RULE: If the firewall is set to deny rule, it will block the connection and send a reset packet back to the requester. The requester will know that the firewall is deployed.
DROP RULE: If the firewall is set to drop rule, it will block the connection request without notifying the requester.
It is best to set the firewall to deny the outgoing traffic and drop the incoming traffic so that attacker will not know whether the firewall is deployed or not.
Question 11: What is the Runbook in SOC?
A runbook, also known as a standard operating procedure (SOP), consists of a set of guidelines to handle security incidents and alerts in the Security Operation Centre. The L1 security analyst generally uses it for better assessment and documentation of the security events.
Question 12: What is the difference between the Red Team and the Blue Team?
Red Team: The red team plays an offensive role. The team conducts rigorous exercises to penetrate the security infrastructure and identify the exploitable vulnerabilities in it. The red team is generally hired by the organization to test the defenses.
Blue Team: The blue team plays a defensive role. The blue team’s role is to defend the organization’s security infrastructure by detecting the intrusion. The members of a blue team are internal security professionals of the organization.
Question 13: Define a Phishing attack and how to prevent it?
Answer: Phishing is a type of social engineering attack in which an attacker obtains sensitive information from the target by creating urgency, using threats, impersonation, and incentives. Spear phishing, e-mail spam, session hijacking, smishing, and vishing are types of phishing attacks.
Question 14: What is the Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attack, and how to prevent it?
Answer: Cross-site Scripting: In the cross-site scripting attack, the attacker executes the malicious scripts on a web page and can steal the user’s sensitive information. With XSS vulnerability, the attacker can inject Trojan, read out user information, and perform specific actions such as the website’s defacement.
Countermeasures:
Encoding the output
Applying filters at the point where input is received
Using appropriate response headers
Enabling content security policy
Escaping untrusted characters
Question 15: Explain the SQL injection vulnerability and give countermeasures to prevent it?
Answer: SQL Injection: SQL injection is a famous vulnerability in the web application that allows hackers to interfere in communication taking place between a web application and its database. Hackers inject malicious input into the SQL statement to compromise the SQL database. They can retrieve, alter, or modify the data. In some cases, it allows attackers to perform DDOS attacks.
Countermeasures:
Using parameterized queries
Validating the inputs
Creating stored procedures
Deploying a web application firewall
Escaping untrusted characters
Question 16: Difference between hashing and Encryption?
Hashing
Conversion of data into a fixed-length of unreadable strings using algorithms
Hashed data can not be reverted back into readable strings
The length of the hashed string is fixed
No keys are used in hashing
Encryption
Conversion of data into an unreadable string using cryptographic keys
strings Encrypted data can be decrypted back into readable strings
The length of the encrypted string is not fixed
Keys are used in Encryption
Question 18: What is the difference between SIEM and IDS?
Both collect the log data, but unlike SIEM, IDS does not facilitate event correlation and centralization of log data.
Question 20: What is DNS? Why is DNS monitoring essential?
DNS monitoring can disclose information such as websites visited by the employee, malicious domain accessed by an end-user, malware connecting to Command & Control server. It can help in identifying and thwarting cyberattacks.
https://www.infosectrain.com/blog/20-most-common-soc-analyst-interview-questions-and-answers/
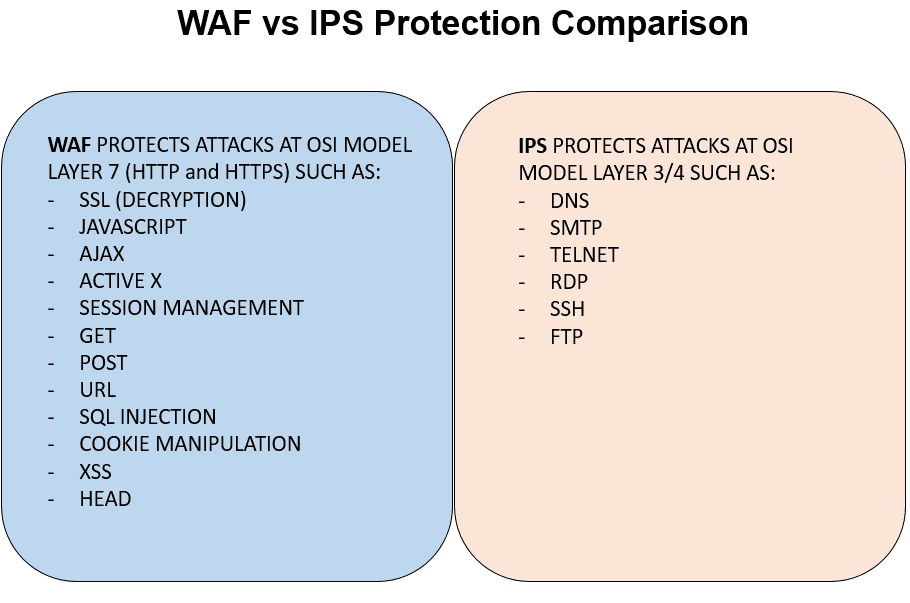
- How does a Web Application Firewall work?
. Which of these protocols is a connection-oriented protocol? The Correct Answer is:- D
- A) FTP
- B) UDP
- C) POP3
- D) TCP
What port range is an obscure third-party application most likely to use? The Correct Answer is:- D
- A) 1 to 1024
- B) 1025 to 32767
- C) 32768 to 49151
- D) 49152 to 65535
Which category of firewall filters is based on packet header data only? The Correct Answer is:- C
- A) Stateful
- B) Application
- C) Packet
- D) Proxy
At which layer of the OSI model does a proxy operate? The Correct Answer is:- D
- A) Physical
- B) Network
- C) Data Link
- D) Application
Which technology allows the use of a single public address to support many internal clients while also preventing exposure of internal IP addresses to the outside world? The Correct Answer is:- D
- A) VPN
- B) Tunneling
- C) NTP
- D) NAT
What item is also referred to as a logical address to a computer system? The Correct Answer is:- A
- A) IP address
- B) IPX address
- C) MAC address
- D) SMAC address
Which of the following is commonly used to create thumbprints for digital certificates? The Correct Answer is:- A
- A) MD5
- B) MD7
- C) SHA12
- D) SHA8
Which of the following creates a fixed-length output from a variable-length input? The Correct Answer is:- A
- A) MD5
- B) MD7
- C) SHA12
- D) SHA8
What encryption process uses one piece of information as a carrier for another? The Correct Answer is:- A
- A) Steganography
- B) Hashing
- C) MDA
- D) Cryptointelligence
Which of the following is a major security problem with FTP? The Correct Answer is:- C
- A) Password files are stored in an unsecure area on disk.
- B) Memory traces can corrupt file access.
- C) User IDs and passwords are unencrypted.
- D) FTP sites are unregistered.
What type of program exists primarily to propagate and spread itself to other systems and can do so without interaction from users? The Correct Answer is:- D
- A) Virus
- B) Trojan horse
- C) Logic bomb
- D) Worm
Which mechanism is used by PKI to allow immediate verification of a certificate’s validity? D) OCSP
- A) CRL
- B) MD5
- C) SSHA
- D) OCSP
Which statement(s) defines malware most accurately? The Correct Answer is:- B,C
- A) Malware is a form of virus.
- B) Trojans are malware.
- C) Malware covers all malicious software.
- D) Malware only covers spyware.
Which is/are a characteristic of a virus? Which is/are a characteristic of a virus?
- A) A virus is malware.
- B) A virus replicates on its own.
- C) A virus replicates with user interaction.
- D) A virus is an item that runs silently.
A polymorphic virus __________. The Correct Answer is:- C
- A) Evades detection through backdoors
- B) Evades detection through heuristics
- C) Evades detection through rewriting itself
- D) Evades detection through luck
A sparse infector virus __________. The Correct Answer is:- C
- A) Creates backdoors
- B) Infects data and executables
- C) Infects files selectively
- D) Rewrites itself





No comments:
Post a Comment