that was the time when very moment the choice wasvery simple: when your analytical database grow beyond 5-7 terabytes in size you justinitiate
No one heard about the “unstructured” data
And as Hadoop became more and more popular, MPP databases entered their descent.
So the question regarding “whether I should choose MPP solution or Hadoop-based solution?”
Many of the vendors are positioning Hadoop as a replacement of the traditional data warehouse, meaning by this the replacement of the MPP solutions.
Some of them are more conservative in the messaging and pushing the Data Lake / Data Hub concept, when Hadoop and MPP leave beside each other and integrating
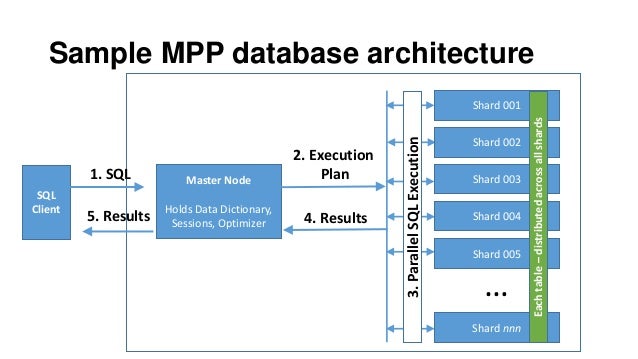
MPP stands for Massive Parallel Processing, this is the approach in grid computing when all the separate nodes of your grid are
MPP DBMSs are the database management systems built on top of this approach. In these systems
One additional advantage that this architecture delivers to you is the scalability, because you can easily scale the grid by adding new nodes into it. To
This further speeds up the processing of the data, because using shared storage for this kind of design would be a huge overkill
The chunks are big and they are read-only
what about the cluster resource management? In contrast to MPP design, Hadoop resource manager (YARN) is giving you more fine-grained resource management
you can conclude why Hadoop cannot
https://0x0fff.com/hadoop-vs-mpp/
- Massively Parallel Processing (MPP) Database on Hadoop
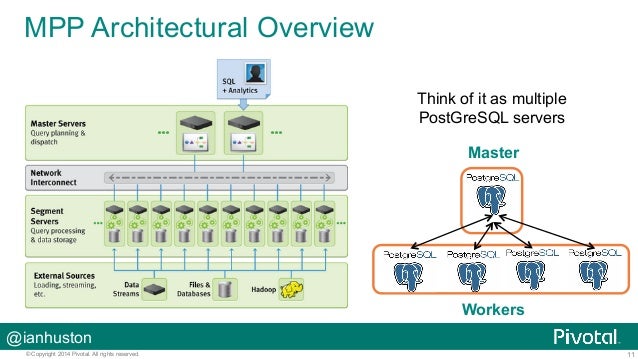
In Massively Parallel Processing (MPP) databases data is partitioned across multiple servers or nodes with each server/node having memory/processors to process data locally. All communication is via a network interconnect — there is no disk-level sharing or contention to
http://www.grroups.com/blog/massively-parallel-processing-mpp-database-on-hadoop
- In Massively Parallel Processing (MPP) databases data is partitioned across multiple servers or nodes with each server/node having memory/processors to process data locally. All communication is via a network interconnect — there is no disk-level sharing or
https://dwarehouse.
- In computing, massively parallel refers to the use of
a large number of . a large number of is opportunistically used . . a large number of in close proximity to Infiniband
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Massively_parallel
- MPP (massively parallel processing) is the coordinated processing of a program by multiple
processor s . An MPP system is considered ( ) a number of be searched
https://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/MPP-massively-parallel-processing
- What is a data lake?
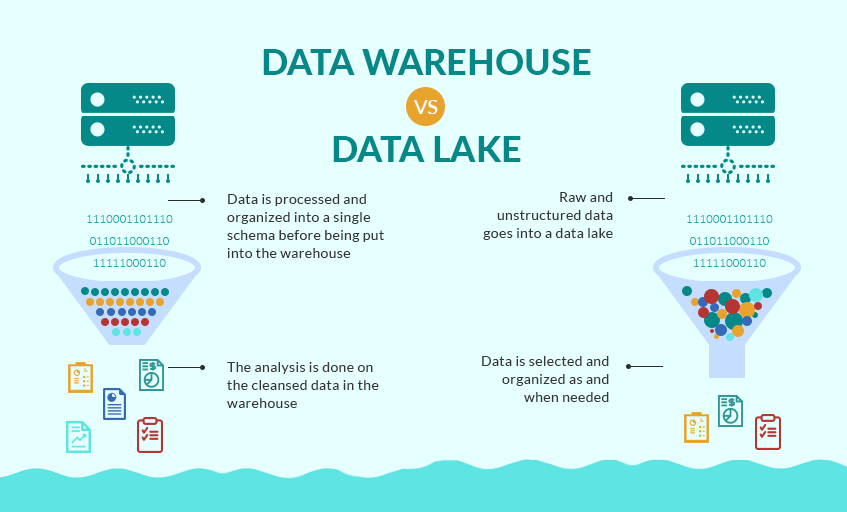
A data lake is a centralized repository that allows you to store all your structured and unstructured data at any scale. You can store your data as-is, without having to first structure the data, and run different types of analytics—from dashboards and visualizations to big data processing, real-time analytics, and machine learning to guide better decisions.
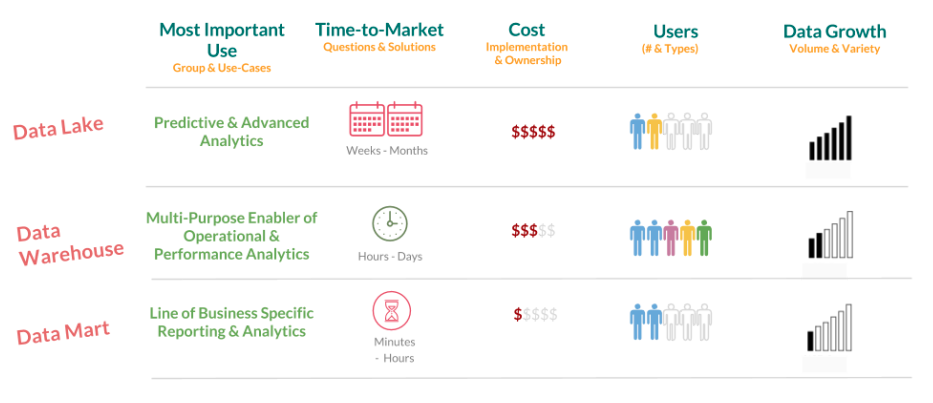
Data Lakes compared to Data Warehouses – two different approaches
A data warehouse is a database optimized to analyze relational data coming from transactional systems and line of business applications. The data structure, and schema are defined in advance to optimize for fast SQL queries, where the results are typically used for operational reporting and analysis. Data is cleaned , enriched, and transformed so it can act as the “single source of truth” that users can trust.
A data lake is different, because it stores relational data from line of business applications, and non-relational data from mobile apps, IoT devices, and social media. The structure of the data or schema is not defined when data is captured . This means you can store all of your data without careful design or the need to know what questions you might need answers for in the future . Different types of analytics on your data like SQL queries, big data analytics, full text search, real-time analytics, and machine learning can be used to uncover insights
https://aws.amazon.com/big-data/datalakes-and-analytics/what-is-a-data-lake/





No comments:
Post a Comment